Long before Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate made its mark in laboratories and industrial plants, chemists hunted for more reliable sulfonating agents. In those early years, sulfonation of aromatic compounds focused on less selective, messy pathways. Around the turn of the twentieth century, the focus shifted to toluene sulfonates, which opened up practical applications in dyes, detergents, and pharmaceutical intermediates. As a sulfonate salt, Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate gained favor for its water solubility and clean conversion process. This journey from research benches to full-scale production lines reflects a huge evolution in organic chemistry, where ease of purification and increased yields mattered just as much as the final product. In the years since, its straightforward synthesis and adaptability have kept it relevant across changing technological needs.
Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate, recognized for its clear sodium salt structure, holds value in more than one niche. Chemists and manufacturers know it as a white to off-white crystalline powder with a sharp sulfonic footprint. Its predictable reactivity, high solubility in water, and readiness in solid or solution form support both laboratory exploration and large-scale processes. Through the decades, the ability to trust its consistency and performance keeps it on procurement lists, whether the job is synthesis, formulation, or research-driven testing.
Under close inspection, Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate reveals itself as more than just a benign powder. It delivers reliable melting at around 288°C and boasts a respectable molecular weight of 216.19 g/mol. In my own time at the bench, I’ve appreciated how well it handles being mixed into aqueous solutions without any fuss—few residues, fewer surprises. Its density of about 1.54 g/cm³ helps with accurate measurement, and the strong aromatic odor rarely escapes the attentive chemist’s notice. Chemically, the sulfonate group on the para-position of the toluene ring sets up reactions with nucleophiles, bases, and many oxidizing agents. Not all chemicals grant this level of versatility so reliably, which makes it a preferred candidate for synthetic routes in various industries.
In bulk shipments and scientific supply catalogs, Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate often arrives stamped with purity above 99%. Sellers keep moisture below defined thresholds; even minor deviations risk clumping and unpredictable flow. For traceability, each container usually bears lot numbers, manufacturing dates, and recommended storage conditions—generally cool, dry places out of direct sunlight. That might sound like standard procedure, but specifics make handling easier and build trust. Labels also carry hazard pictograms and signal words, not as bureaucratic filler, but to warn of respiratory or skin irritation risk if protocols slip. For those working hands-on, this information keeps accidents at bay and meets regulatory requirements from agencies in the US, EU, and Asia.
Scaling the synthesis of Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate involves direct sulfonation of toluene with concentrated sulfuric acid. After reaction completion, neutralization with caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) converts the acid to its sodium salt. From pilot lab to industrial reactor, this method’s reliability links to careful control of temperature and acid strengths. Mononitration remains a minor risk unless temperatures rise unchecked. Steady stirring and gradual addition of the base keep the exotherms low, limit splattering, and create clean end-product. Operators drain off the aqueous phase, isolate the solid, and wash it repeatedly before drying. A crystalline powder emerges, ready for distribution. Knowing exactly where complications might arise—like foam formation or hydrolysis—shows the road between chemistry theory and real-life practice is sometimes anything but straight.
In synthetic chemistry, the true colors of Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate show up during downstream reactions. Whether it acts as a nucleophile or electrophile, the para-sulfonate substituent draws in partners for efficient displacement and coupling. In my hands, it has served capably in nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions, helping build more complex aromatic structures for specialty chemicals and dyes. Under alkaline conditions, its aromatic ring stays intact, and the sulfonate group proves more stable than other leaving groups. It lends itself to simple modifications—such as conversion to the corresponding acid, esterification, or transformation into more exotic sulfone linkages. Chemical engineers keep this versatility top of mind; tailoring downstream chemistries to precise product requirements gets a whole lot more manageable.
Beyond the standard “Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate” handle, this compound shows up under “Sodium p-Toluenesulfonate,” “p-Toluenesulfonic Acid, Sodium Salt,” and “4-Methylbenzenesulfonic Acid, Sodium Salt.” Pharmaceutical and specialty chemical catalogs sometimes shorten names or rely on internal codes. By whatever name, buyers and users chase only verified chemical identity through consistent structural formulas and batch testing. Choosing a trusted supply source means sidestepping problems from off-spec or poorly documented material—mistakes that cost time and money, or worse, risk regulatory penalties.
Chemists working with Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate respect its moderate risk profile and build controls accordingly. Inhaled dusts can irritate airways or trigger allergies, so lab coats, splash goggles, and quality gloves stay close at hand. Spills sweep up easily with damp cloths to avoid airborne particles, and proper ventilation vents away any incidental fumes. Regular attention to MSDS details—signal words like ‘Warning’—keeps workers informed about environmental impact and first aid measures. Storage rules recommend keeping containers sealed tight to cut down on moisture gain, as clumping only leads to inconsistent dosing and messier workspaces. Regulatory documentation—covering everything from permissible exposure limits to waste disposal—backs up safe handling, and most experienced chemists see these standards as an extension of their personal safety protocols.
Across a busy landscape of industries, Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate finds recurring roles as a chemical intermediate, phase-transfer catalyst, and crystallization agent. Textile manufacturers put it to work in dyeing operations, where its affinity for fibers helps build strong, lasting color. Water treatment specialists use it to modify surfactant properties and alter precipitation rates in cleaner production. Pharmaceutical teams depend on it during synthesis of sulfonamide antibacterials and sulfa-based drugs. Through my own experience collaborating with detergent makers, its legacy as a processing aid and buffer for pH adjustments demonstrated just how widespread its applications remain. These varied uses mean that quality, purity, and on-time supply go hand-in-hand—any breakdown in one spot might sideline production elsewhere.
Research circles see Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate as both a reliable workhorse and a springboard for innovation. With a stable sulfonate group and familiar aromatic character, it underpins research into new ligands, advanced ion-exchange resins, and hybrid materials. Environmental scientists explore its fate as a tracer for studying water movement or contaminant dispersal. High-throughput screens in pharmaceutical labs sometimes include it as a synthetic block because of its tolerance for harsh conditions and varied reactivity. Its behavior in radical and electrophilic conditions has shaped thinking in reaction engineering, fueling more efficient catalytic cycles. These developments thrive through transparent sharing of research findings, cross-checking of analytical data, and collaboration with regulatory watchers who keep public health and environmental impact in mind.
Attention toward toxicity hinges on Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate’s ability to irritate eyes, skin, and respiratory passages. Acute toxicity studies in rodents show relatively high LD50 values, with little evidence for chronic toxicity or carcinogenic risk under standard handling conditions. Ecotoxicology work remains ongoing; its water solubility means monitoring environmental release matters, especially near large-scale facilities. In my days auditing safety data, routine wastewater testing and effluent controls featured prominently, since regulators want any new chemical input characterized ahead of approval. Knowledge on biodegradation, persistence, and aquatic impacts continues to build through academic and industrial partnerships, forming the evidence base for safe use and responsible disposal.
New waves in materials science and green chemistry look toward Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate not just as a legacy compound but as a pivot point for sustainability. Forward-thinking process engineers seek efficient sulfonation strategies to reduce energy costs, cut waste, and raise atom economy. Exploration of its use in ionic liquids, advanced nanomaterials, or as a precursor for biodegradable surfactants promises to keep it in demand. Broader engagement with life cycle analysis, alternative solvents, and scalable green synthetic pathways will shape both its use and regulatory landscape. For researchers and manufacturers, adapting workflows to address climate and safety goals means revisiting old favorites like this sulfonate, finding new relevance in a constantly shifting market.
Sodium toluene-4-sulphonate doesn’t catch headlines or become a topic at dinner tables. Still, plenty of industries rely on it. You can trace it back to manufacturing lines, water treatment, textile plants, and laboratories. The name sounds like a tongue-twister, yet the uses untangle surprisingly fast once you walk through a factory door or examine an everyday product label.
The textile world often turns to sodium toluene-4-sulphonate to help dyes dissolve and spread smoothly. In my summer job at a garment plant, a supervisor showed me how synthetic dyes needed help soaking into massive spinning vats of water. If you simply dump dye powder into a tub, you tend to get clumps and faded shirts. This chemical steps in, interacts with dye molecules, and boosts their ability to dissolve. The end result is cleaner, brighter prints and fewer rejected shirts on the line. Many times, what starts as a lab experiment ends up shaping the look and quality of clothes on store racks.
Many laundry and cleaning formulas need a balance of chemicals to work well. Surfactants let water and oil mix so greasy residues lift out of fabric or off dishes. Sodium toluene-4-sulphonate acts as an additive or processing aid, making sure these mixtures don’t separate. The difference becomes clear after seeing a soap that leaves streaks or a detergent that doesn’t rinse out fully. Every time this chemical does its job, it makes cleaning more consistent for regular homes, not just industrial floors.
Drug developers aim for pills that dissolve at the right rate in the stomach or bloodstream. Sodium toluene-4-sulphonate sometimes appears as an excipient—a helpful companion ingredient. It makes tricky substances more soluble and easier to mix. This step also matters for safe dosing and reducing side effects. The behind-the-scenes work of people in pharma labs, and the precision chemicals they use, shape much of the medicine cabinet at home.
Industrial wastewater contains tricky residues and surfactants. Sodium toluene-4-sulphonate helps as a dispersing agent, breaking stubborn particles or organic bits into smaller pieces, speeding up filtration. Clean water matters to everyone downstream. Municipal plants rely on such chemicals, not just heavy equipment, to meet regulatory targets and keep rivers safer.
We cannot ignore calls for more responsible chemistry. Studies highlight that sodium toluene-4-sulphonate shows low toxicity to people at usual exposure, yet some byproducts need careful handling. Spills or sloppy disposal can still cause soil or water trouble. This means training, clear labeling, and responsible supply chain choices across the board. The shift toward greener, less persistent additives puts a spotlight on evaluating every ingredient, not just headline toxins.
You spot progress in policies, packaging, and research journals. Companies are investing in wastewater recycling and stricter audits. Educational groups run programs for factory workers about basics like chemical compatibility and emergency plans. There's talk about replacing older chemical processes with more biodegradable options where possible, and adapting quality standards as new data comes in. Real change grows from repetitive, practical efforts—the clipboard checks, the in-person trainings, the push for clear labeling. Much of this happens quietly and out of public view, but it shapes every cleaner shirt, every washed plate, every safe glass of water.
Anyone who has worked in a real lab knows that shortcuts around safety don’t end well. Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate, commonly used in dyes and as an intermediate for chemical synthesis, doesn’t sound dangerous at first. Yet, treating it like ordinary table salt is where accidents find their opening. It can cause irritation and trigger allergies. Keep exposures short and protect your skin, eyes, and lungs when this compound comes out.
Start with the basics. A kid who learned to cook wouldn’t grab a hot pan without a mitt, so don’t handle a chemical like this with bare skin. Pull on nitrile gloves. Lab coats aren’t about impressing visitors; they keep splashes off your clothes and skin. Eye protection blocks out flying dust or accidental splashes, which sounds minor until it happens to you. Goggles beat regular glasses. Dust inhalation may look harmless at first glance. A dust mask or, even better, a full respirator in powder-heavy environments stops particles before trouble starts.
Good air flow isn’t just a box on a checklist. Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate’s dust should never hang around longer than it takes you to notice it. Chemical fume hoods protect everyone in the room, so keep work to the hood or a lab bench with proper extraction. Cleaning up as you go makes tomorrow’s work smoother and prevents sneaky spills from growing into bigger messes.
Don’t just toss this compound under the bench to save time. Store in sealed, labeled containers made for chemicals. Moisture and incompatible substances in the same space set up more risk. Keep acids, oxidizers, and bases apart. I once saw a shelf where every bottle looked the same. Clear, honest labeling—name, date, hazards—saves confusion during an emergency, and makes sure you pitch the right bottle at clean-up.
Spills never respect your schedule. Spill kits with absorbent materials and dedicated waste bins stop spread instantly. Don’t sweep powder into a drain. That only pushes the problem down the line—quite literally, since some compounds don’t break down easily. Chemical waste, even for “low risk” materials, belongs in dedicated disposal, picked up by professionals who know the regulations. Based on experience, the paperwork from a spill takes far longer than the extra few seconds spent using the right bin.
Book knowledge fades under stress, but running an emergency drill makes people act fast. Anyone working with Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate should know the emergency shower, eyewash station, and exits by heart. Print up-to-date safety data sheets and keep them posted in plain sight—nobody grabs a file on their phone with chemical all over their gloves.
Leaning into regular safety reviews and making safety part of the workflow means mistakes stay rare. Labs that use this chemical often set up buddy systems—someone always has your back and double-checks storage and clean-up. Better signage, smart labeling with QR codes for safety data, and investing in better personal protective equipment help cut down on simple errors. Practical know-how, not just posted rules, shapes a safer, smoother lab.
The name Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate doesn’t sound friendly to most folks. Many people come across chemicals like this in their daily work, especially if they’re in water treatment, manufacturing, or working with dyes. For a long time, I worked at a print shop, and our supply closet always seemed crowded with mystery powders and solutions. It taught me to read up on any chemical that went near people, drains, or the garbage can. So, weighing the dangers isn’t just academic — sometimes, it’s about keeping skin, lungs, and rivers healthy in real life.
Looking at research and safety data, Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate hasn’t shown the kind of toxicity some industrial substances are known for. Acute effects rarely show up unless someone gets it in their eyes or breathes in dust during work. The risk jumps up if there’s a spill and no one uses gloves or goggles. For people with asthma or allergies, dust and strong odors can bring out wheezing or rashes. The US Environmental Protection Agency hasn’t called it out for severe consequences from single exposures. Still, just because something isn’t labeled “deadly” doesn’t make it totally safe.
Once chemicals leave the workplace, the next question lands in the river, field, or landfill. Runoff from cleaning tanks or production floors can flow straight into water sources without much warning. Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate can dissolve in water fast. Studies tracking this compound show it tends to break down gradually, especially if exposed to bacteria found in most rivers. But if used without any control, it can build up and disrupt aquatic life. Fish and smaller animals often show strange behavior and slow growth in polluted water. Even if direct poisoning isn’t always recorded, the change in water chemistry isn’t harmless. It’s the buildup over time that sneaks up on plants and critters further down the chain.
Unsatisfying as it sounds, many chemicals only get a full verdict after years of use. Regulations play catch-up, and manufacturers sometimes keep using a compound out of habit unless something bad gets reported. Better labeling and tougher controls mean fewer surprise headaches for workers and fewer toxins heading down the drain. I once helped run emergency drills for chemical spills, and during the practice, no one thought much about the powder on the floor. Months later, a real leak brought home just how quickly these substances can spread. Even one overlooked bag led to a panic — skin irritation, worried parents, shaky employees. If places using this chemical give workers regular safety training and offer proper masks and gloves, problems drop dramatically.
Some practical changes make a real difference. Regular inspections in factories can spot sloppy storage or outdated containers. Wastewater testing gives early warning on chemical escapes. Switching to less hazardous alternatives where possible lowers risk for everyone. Public reporting of chemical use builds trust, and lets people in local neighborhoods keep tabs on what’s floating in their streams or winds up near playgrounds. Simple steps, like teaching workers to spot warning signs or enforcing cleanup rules, work better than waiting for a disaster to force change.
People have created safer, more transparent workplaces by speaking up about little spills, drips, and fumes. Everyone, from line workers to office teams, can push to learn what’s in their tools and push for clear answers from suppliers. Staying informed helps catch problems before they grow, and new research or guidelines should show up in staff meetings, not just academic journals. By treating “safe enough” as an ongoing job, the risks around Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate — or any chemical — shrink, for employees and for the world beyond the factory gates.
Plenty of products get tossed around in labs and factories with long, tongue-twisting names. Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate can sound intimidating until you break down what it actually is. The chemical formula, C7H7SO3Na, doesn’t just sit on a label for show. Every symbol and number packs information that can save people from costly mistakes, contaminated mixtures, and failed experiments.
Let’s run through it plainly. The formula tells us the makeup: seven carbons, seven hydrogens, one sulfur, and three oxygens, tied together with a sodium atom. If you’re handling a big batch of a compound, you double-check the exact make-up each time a new order comes in. Relying only on supplier promises sets you up for disappointment and thin excuses, especially if you work in water treatment or chemical formulation.
Getting the molecular weight spot-on matters. Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate clocks in at about 194.18 grams per mole. Not knowing that number leads to wasted time and ruined batches. I once watched a friend botch an entire day’s lab work by using the wrong weight because he pulled data off an unreliable source. Trustworthy information helps professionals prepare solutions correctly, dose materials right, and calculate how much of a substance interacts with something else.
A lot of folks think numbers like 194.18 or C7H7SO3Na matter only to the “chemistry nerds.” Truth is, they crop up for anyone mixing large volumes, whether in a small research project or scaling up industrial production. If you’re running a wastewater plant or testing for pollution, ignorance of the formula can throw off entire runs of data, leading to either compliance fines or environmental damage.
One missed atom—or a tiny miscalculation—affects how the compound dissolves, reacts, or even stores. Imagine risking your permits, contaminating your product, or failing a whole inspection because a supplier mislabeled a bag.
Let’s not pretend labs always have up-to-date records. Periodically checking the label against up-to-date reference databases protects against small mistakes that spiral into expensive fixes. Citing sources like Sigma-Aldrich or PubChem, rather than taking the easy route with the first Google result, could save thousands over a year.
Cross-verifying the molecular weight keeps dosing on target and results consistent. In my own experience, updating our standard operating procedures with CAS numbers and clear formulas reduced confusion for new hires. Training staff to double-check rather than relying on “what we did last year” builds a smarter team, one less likely to repeat past errors.
Chemical errors don’t always make headlines, but they should. Mistaking one compound for another—or fudging the numbers—risks not just money, but safety. Slow leaks, failed toxicology screens, and supply chain headaches usually trace back to missing or incorrect chemical data.
Being obsessive about chemical formulas and molecular weights isn’t perfectionism—it’s about keeping costs in check and products safe. Compounds like Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate demand attention because regulations, customers, and the environment aren’t forgiving.
Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate helps keep chemical production running at full tilt. Folks working in dye, pharmaceutical, and detergent plants see these bags and drums stacked everywhere. On the surface, the job looks simple: just keep the product dry and move it with care. In reality, small mishaps—cracked bags, a leaky roof, damp air creeping in—can throw entire batches off, costing big money and putting staff at risk.
Nights working in chemical warehouses, it didn’t take long to see how critical humidity control stays. Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate pulls in moisture from the air, forming wet clumps that jam up machinery. No one wants to explain a clogged pump or spoiled drum to the plant manager in the morning. Each extra ounce of water is a chance for spoilage or, worse yet, dangerous microbial growth—no joke in a facility that runs around the clock.
Smart operators take storage rooms seriously. Dehumidifiers run non-stop, and temperature monitors hang everywhere. Silica gel packs get tossed into drums as extra insurance. Every worker who handles the product gets a safety rundown: keep the bag sealed and stash it on skids off the ground. Pallets get checked for mold and damage before new shipments land. Any shortcut on this routine, and the company hears about it soon enough.
Reading chemical labels sounds bureaucratic, but it spares a lot of chaos. Back in the day, I watched a new guy dump the product into the wrong tank. There was a scramble, alarms blaring. All from faded, unreadable tags. Clear hazard labels—corrosive, keep dry, non-flammable—stick right to the drums. Workers can check the label instead of guessing. This single step has stopped plenty of mix-ups and emergency room visits.
Too often, drivers treat chemical loads no different than cases of bottled water. For Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate, this mistake ends in product loss or contamination. Closed trucks, away from rain and sun, block out temperature swings. Any transport break-down puts the whole load at risk, since moisture or heat can sneak in. Trained drivers know not to stack the product near acids or oxidizers, and they carry spill kits on long trips.
Shortcuts and cost-cutting rarely pay off. I’ve seen trucks halted at the warehouse because drums sat out in the rain for half an hour, soaked through. Salvaging that load costs more than checking truck seals or tarps before leaving the plant.
The real fix for smoother storage and transport comes down to routine and respect for the rules. Staff training cannot become a box-ticking exercise; regular workshops keep the basics fresh in everyone’s mind. Maintenance beats repair—spotting a rusty drum or faulty seal avoids far bigger disasters.
Companies can invest in better tracking tech, such as barcodes or sensors, to log temperature and humidity along the shipping route. Transparency here doesn’t just please the auditor—it protects everyone who touches the supply chain. Each extra step protects health, budgets, and production schedules. In an industry pressed by tight deadlines and high expectations, getting the basics right with Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate gives everyone a fighting chance to keep things running safely.
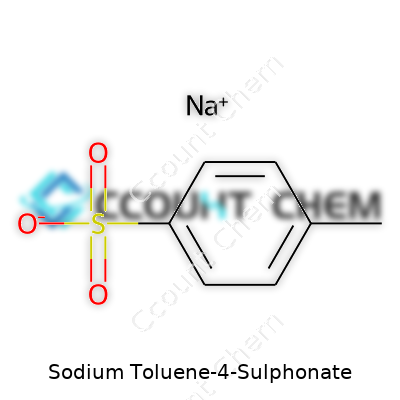
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | sodium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate |
| Other names |
Tosylate sodium Sodium p-toluenesulfonate Sodium tosylate Sodium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate |
| Pronunciation | /ˈsəʊdiəm tɒl.juː.iːn fɔː ˈsʌl.fə.neɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 657-84-1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | `3D model (JSmol)` **string** for **Sodium Toluene-4-Sulphonate**: ``` CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] ``` *(This is the standard SMILES string you can use for 3D visualization in JSmol or similar molecular modeling tools.)* |
| Beilstein Reference | 1909592 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:8737 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2106901 |
| ChemSpider | 16459 |
| DrugBank | DB11372 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.321 |
| EC Number | 204-889-2 |
| Gmelin Reference | 82278 |
| KEGG | C01738 |
| MeSH | D013014 |
| PubChem CID | 8611 |
| RTECS number | WL6475000 |
| UNII | E016XO823L |
| UN number | UN2585 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DJ6VX6608L |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H7SO3Na |
| Molar mass | 216.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Soluble in water |
| log P | -2.2 |
| Vapor pressure | Negligible |
| Acidity (pKa) | -2.8 |
| Basicity (pKb) | > 11.04 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -49.0e-6 cm³/mol |
| Dipole moment | 3.2 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 362.8 J·K⁻¹·mol⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -617.0 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -802.5 kJ·mol⁻¹ |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | A01AD11 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | May cause eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS07, GHS09 |
| Pictograms | GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302, H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | Precautionary statements: P261, P305+P351+P338, P304+P340, P312 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-1-0 |
| Flash point | > 150°C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | Oral Rat LD50: >2000 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (oral/rat): 2480 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | SW6825000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 10 mg/m³ |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Toluene-4-sulfonic acid p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride Sodium benzenesulfonate Potassium toluene-4-sulfonate Toluene Benzenesulfonic acid Sulfanilic acid |