Chemistry often throws up unsung workhorses in industrial and consumer products, and sodium cumene sulfonate fits that bill. Looking back to the early days of synthetic detergents, chemists turned to sulfonates after natural soap ran into trouble with hard water. Laboratories sought compounds that helped keep liquids stable and clear, leading to the first practical applications of alkyl aryl sulfonates. The 20th century’s post-war industrial expansion saw sodium cumene sulfonate gain ground as a useful hydrotrope. By the late 1970s, it became a crucial ingredient for formulating cleaning agents that work well in a wide range of water conditions. This innovation gave industry a versatile building block that could bridge the gap between performance needs and cost constraints.
A closer look at sodium cumene sulfonate shows an ingredient with a simple but effective job—help other chemicals do theirs. In most liquid household cleaners and industrial formulations, it steps in as a solubilizer. By coaxing otherwise stubborn or thick surfactants into solution, it delivers clarity and stability. Its use isn’t limited just to household settings. Industrial processes, textile treatment, and agrochemical blends all quietly rely on it. Anyone who has handled powder-to-liquid concentrates or seen a detergent bottle that resists cloudiness has probably benefited from it.
This compound lands in the form of a white, crystalline powder or clear solution. Water acts as its friend, dissolving it quickly. The molecular structure involves a benzene ring with an isopropyl group and a sulfonate, giving good hydrotropic capacity. Sodium cumene sulfonate stays pH-neutral in dilute concentrations, usually ranging in pH from 7 to 9. It stands up to heating and moderate acid or alkaline conditions. Some sodium salts struggle with caking or dusting, but this one stores well, so long as it stays dry.
Accuracy and transparency guide the labeling practices for sodium cumene sulfonate. Product labels run with a CAS number, purity rating—often above 95%—moisture content, and bulk weight. International shipping rules and regional chemical inventories require traces of benzene, sulfate, and CHNS (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur) analysis. Guidelines in the EU and North America usually set limits on aromatic amines and heavy metals. Physical properties such as melting point, solubility profile, particle size distribution, and sodium content often make or break batch approval, especially for high-grade formulations.
The factory route to sodium cumene sulfonate starts with cumene—an isopropylbenzene—through a sulfonation reaction with either fuming sulfuric acid or oleum. The process isn’t gentle; controlling temperature and reaction time stops unwanted byproducts like polysulfonation. Next comes neutralization, where sodium hydroxide steps in. Operators then purify the resulting salt using repeated washes and sometimes vacuum drying. Problems crop up with impurity removal and odor control, but process optimization and closed systems have closed much of the gap. Many plants recover heat and minimize wastewater, reflecting a shift towards greener chemistry.
Chemists working with sodium cumene sulfonate have explored how it partners with surfactants, solvents, and even enzymes. In laboratories, the sulfonate group often gets traded or protected during synthesis, giving rise to novel derivatives. Its backbone supports alkyl chain branching, tweaking foaming and wetting properties. Trials have seen modification with longer alkyl chains to stretch hydrotropic power, but higher costs and marginal gains often rule this out for large-scale production. Its aromatic ring also opens up options for coupling with dyes, polymers, and catalysts, although such uses rarely show up outside specialty laboratories.
Chemicals often take on more than one name depending on the manufacturer or country of sale. Sodium cumene sulfonate also appears as sodium isopropylbenzenesulfonate or simply SCS. Brands in North America and Europe sometimes call it by a trade name ending in the letters “NP” or “IPBS.” Chemical supply catalogs might list synonyms like benzene, (1-methylethyl)-, sulfonic acid, sodium salt (1:1) or sodium 2-(1-methylethyl)benzenesulfonate. Specialty producers stamp distinctive codes on labeling for tracking batches, keeping recalls or traceability in reach if problems break out.
Factories take chemical safety seriously, and sodium cumene sulfonate’s Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) reads as practical advice. Powered by years of research on sulfonates, proper use avoids inhaling powders, limits skin exposure, and prioritizes eye protection. In my own workspaces, we handled the powder with masks and nitrile gloves—basic, sensible steps. Spills clean up with water, but large quantities need bundling and careful waste disposal. Fire risk stays low, thanks to non-combustibility, though decomposition throws up sulfur oxides if temperatures soar. Product tankers and storage silos get regular inspection against corrosion and leaks as standard practice.
The reach of sodium cumene sulfonate extends farther than most realize. Leading detergent makers use it to push up the cleaning action of both powdered and liquid formulas. In agriculture, it boosts solubility and stability for pesticides and herbicides, allowing for concentrated liquid blends that spread evenly on crops. Textile processors rely on it to improve dye acceptance or help with scouring. Water treatment engineers favor it to disperse oily residues in industrial wastewater or maintain clear circulating water during manufacturing. Oilfields sometimes use the compound to thin drilling fluids or break up emulsions, reducing downtime in extraction. Each field leverages its hydrotropic effect without needing exotic conditions or complex blending protocols.
Research into sodium cumene sulfonate keeps evolving, especially as markets shift toward greener chemistry. Laboratories test new synthetic pathways that use lower-temperature sulfonation or alternative feedstocks, eyeing a future less tied to crude oil derivatives. Teams at universities and manufacturers run side-by-side comparisons against newer hydrotropes, looking for higher solubility or lower toxicity. Many results turn up in open-access journals or patents, part of a broader movement toward transparency around industrial chemicals. These investigations often feed into guidelines for exposure, suggesting upper limits for use in specific applications and ways to recover or recycle the compound at the end of its working life.
Safety research stands as a central concern for commercial chemicals. Toxicological studies point out that sodium cumene sulfonate shows low acute toxicity by oral, inhalation, and dermal exposure routes. Standard laboratory animals took oral doses well above likely workplace or consumer exposure without suffering long-term effects. Eyes and skin show some irritation at higher concentrations, but not enough to class it as a major hazard. Chronic studies and aquatic toxicity work put its risk profile in line with other common cleaning ingredients. More journals now pressure for wider seen chronic and ecological tests. Discussion among regulatory bodies shapes guidelines for maximum discharge and encourages producers to minimize losses in wastewater outflow.
Higher environmental standards and consumer demand for “cleaner” labels force industrial chemicals to adapt. Sodium cumene sulfonate can ride this change, so long as supply chains tap into more sustainable cumene sources and producers limit waste. There’s growing interest in using biotechnology to create similar hydrotropes from renewable feedstocks. Analysts also push for packaging reform—safe transit of bulk powder, sturdy drums for liquid, and ways to reclaim used containers—rather than seeing more plastics hit landfills. The chemical’s straightforward chemistry still leaves room for blend innovations, supporting multi-function cleaning products that reduce overall chemical load without lowering performance. In the hands of responsible producers and practical regulators, sodium cumene sulfonate holds onto its role for another era of industrial and consumer products.
Walk down any supermarket aisle, pick up a laundry detergent or an all-purpose cleaner, and you’ll likely see a list of chemicals most folks can’t pronounce. One ingredient that quietly pulls a lot of weight is sodium cumene sulfonate. This name doesn’t exactly spark excitement, but it plays a practical role in daily life.
Sodium cumene sulfonate serves as a solubilizer. Imagine throwing sugar into a glass of cold iced tea—it’s tough to dissolve. Now picture mixing oil-based fragrances or detergents with water. The same stubbornness happens. Sodium cumene sulfonate steps in and helps these pieces mix smoothly, turning a clumpy mess into something that looks, pours, and cleans better. The result is a stable, clear liquid that folks want to use.
In my own home, hard water sometimes leaves a cloudy residue in the sink and on dishes. Before I learned about the real role of ingredients like sodium cumene sulfonate, I assumed a cleaner was just about soap and scent. But this ingredient boosts the power of surfactants—the part of the cleaner that grabs grime and rinses it away. Without sodium cumene sulfonate, even “concentrated” cleaners might separate or lose their punch.
The big players in cleaning products like P&G and Unilever rely on sodium cumene sulfonate for this reason. They mix it into liquid detergents, surface sprays, and dish soaps. According to industry analysts, even a small percentage can make a big difference in shelf stability and cleaning action.
People often worry about chemicals in cleaners. Safety studies on sodium cumene sulfonate show it’s pretty mild. Unlike some older additives, it doesn’t stick around in the environment or bioaccumulate where it shouldn’t. Toxicologists have found it’s safe for skin contact in the concentrations used in cleaning products. So, it helps keep the peace between strong cleaning and personal safety—a tough balance manufacturers have to strike.
Manufacturers today try to cut down on water and packaging waste. Sodium cumene sulfonate lets them design concentrated formulas that dissolve in less water and ship more efficiently. Smaller bottles, less plastic, and less energy to transport are all real wins, especially for a planet where every shipment counts. Reports from sustainability officers at larger firms show measurable reductions in carbon footprint after switching to stronger, more concentrated blends.
No chemical is perfect. Some wastewater treatment plants flag certain sulfonates, and sodium cumene sulfonate belongs to this group. Industry groups keep pressure on manufacturers to lower the amounts and use better water treatment. Continual research into biodegradable alternatives also keeps the ingredient in check, so progress doesn’t stall out.
Most people may never notice sodium cumene sulfonate, but its presence shapes products people use every day. By helping everything blend, protect surfaces, and stay shelf-stable, this ingredient carves out a lasting place in the cleaning aisle. Solid science, a good safety track record, and a push for better environmental practices mean it’s likely to stick around, even as companies keep searching for greener options.
Sodium cumene sulfonate shows up on the back of many shampoo, hand soap, and shower gel bottles. It works by helping other ingredients blend, so products feel light, not heavy or greasy. It gets used to thin out thick mixtures, which often means you use less water. This chemical’s roots trace back to the petroleum world, but after processing, it’s a whole different compound. Science says its job is to make products smoother and more effective, not hazardous.
Most folks worry when they see a complicated chemical name, but reliable safety data helps ease those fears. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) panel in the US and the European Commission’s Cosmetics Regulation both gave sodium cumene sulfonate a green light after reviewing its effects. They looked at everything from skin reactions to its chance of getting into the bloodstream, and the evidence stacks up well for safety in standard amounts.
I dug into real reports, not hearsay. Safety tests for skin show this ingredient doesn’t cause harmful reactions for most people even at higher concentrations than you’d find in soap or face wash. Only at way-above-normal doses—think almost pure form—did testers see any irritation. Most shampoos and similar products only contain a small fraction of that.
People with ultra-sensitive skin might still get a mild itch or dryness. I’ve tested a lot of body care products over the years and can vouch for the annoyance of mystery breakouts. Usually, fragrance or color additives turn out to be the culprit, not sodium cumene sulfonate. Still, every body is unique. For those intensely sensitive, patch testing on a small area serves as a safe bet before switching to a new brand.
Anyone who tunes into ingredient safety usually cares about what ends up rinsing down the drain, too. Sodium cumene sulfonate does break down in waste treatment plants, so large-scale harm doesn’t show up on global monitoring maps. Current wastewater science shows it doesn’t stick around long enough to pose a problem in rivers or oceans, especially compared to other chemicals from industry and agriculture. Regulations back this up, requiring companies to test the environmental effects as part of doing business.
Ingredient safety depends on how much gets used. Regulators set upper limits on every batch that goes into personal care products. If you stick with store-bought options from reputable brands, the risk stays low. I always check out product recalls and consumer safety alerts; I’ve never seen a credible warning linked to sodium cumene sulfonate from a government body.
A lot of debate in skincare focuses on avoiding unfamiliar names, but real-world science and regulation provide the confidence that ingredients like sodium cumene sulfonate belong in daily routines for most people. If you’re passionate about keeping your personal care both safe and effective, reading labels, checking up on the science, and choosing brands transparent about their testing gives you solid ground to stand on.
Anyone who deals with dirty clothes knows clean laundry depends on more than just a scoop of powder or a splash of gel. Detergents ship out daily to homes and laundromats, all promising that same goal: make life’s spills and stains wash away. Many people never realize just how much work goes on at the molecular level to make that promise stick, especially in the wide world of additives and boosters. Sodium cumene sulfonate is one of those ingredients that rarely earns a headline, but it’s always doing its job in the background, making those sudsy washes effective and easy to use.
Over the years, in my time learning how cleaning products are made, I noticed that every well-performing laundry detergent has a team of helpers besides the main cleaning agents, like surfactants. Sodium cumene sulfonate works as a solubilizer. In plain terms, it helps keep all kinds of ingredients evenly mixed together, especially those that would otherwise separate or clump. Think about making a vinaigrette: shake up vinegar and oil with something like mustard, and they finally blend. Sodium cumene sulfonate does a similar job for cleaning products. By allowing more water-insoluble ingredients to “get along” in the bottle, washing becomes more consistent, especially in hot or cold water or in hard or soft water zones.
Manufacturers rely on sodium cumene sulfonate to cut costs, too, because it lets them mix more affordable raw materials without sacrificing smoothness or consistency in the product. Anyone who’s poured detergent from a bottle that left behind globs or uneven streams knows how frustrating it can be. This additive improves liquid flow, so you pour out every drop easily. For powders, it stops caking and helps everything dissolve fast, so grains don’t linger at the bottom of the wash or feed unwanted residue into the next load.
I spoke to someone working in a detergent plant in the Midwest, and he said sodium cumene sulfonate is on almost every blend list—not because it’s flashy, but because nothing steps up quite like it when companies push to keep up with today’s dense, high-performing formulas. More brands move away from old-fashioned phosphates and look for alternatives that meet safety standards. Sodium cumene sulfonate fits well into this new picture, offering a low-toxicity, biodegradable helper that meets regulations in North America, Europe, and Asia.
There’s always a new wave of scrutiny about what goes down the drain. Most research shows sodium cumene sulfonate breaks down in the environment faster than many of its ancestors. As public concern grows about microplastics, endocrine disruptors, and other chemical waste, choices like this one gain more attention. Toxicologists note it does not bioaccumulate and rarely shows up in groundwater or as a byproduct in animal tissue. It shouldn’t irritate the skin or cause respiratory problems when used as intended, making it a better partner in family homes and public laundry spaces.
There’s work ahead for chemists and companies, especially as regulations shift in response to new data about environmental safety. Strong partnerships between researchers and consumer watchdogs help keep formulations both effective and safe. Sodium cumene sulfonate continues to play a vital role, but transparency about all ingredients, clearer labeling, and better consumer education will always be worth the effort—cleaner laundry shouldn’t come at a hidden cost.
Sodium cumene sulfonate pops up more often than you’d think. It lives in laundry detergents, cleaning sprays, and sometimes even shampoos. This chemical helps other ingredients blend and keeps the formula liquid, which matters when you’re scrubbing kitchen counters or tossing a load of towels in the wash.
Plenty of people talk about cleaning products and their impact on rivers, lakes, and oceans. The spotlight often turns to what companies add to these bottles—especially whether those ingredients break down or stick around. So, what happens once sodium cumene sulfonate leaves your sink or shower?
Based on testing by scientists and government agencies, sodium cumene sulfonate usually breaks down in the environment. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) lists tests that show how fast this compound degrades once bacteria and fungi get to work. In many cases, these trials show that microbes finish the job in a few weeks.
Having spent years researching ingredient labels for household cleaners, I’ve learned that not every “sulfonate” is built the same. Some linger much longer than promised. Sodium cumene sulfonate, though, has a better track record. Its chemical structure includes a benzene ring and a sulfonate group, but bacteria can still attack and split the molecule over time, especially if enough oxygen is present in the soil or water.
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and other environmental bodies rate sodium cumene sulfonate as “readily biodegradable” in standard testing conditions. That rating usually means most of the substance will vanish after a month in an active ecosystem like a wastewater treatment plant or healthy river.
A few years ago, I spent a summer helping test water downstream from a city wastewater plant. Detergents flowed in every morning, swirling with plenty of these surfactants and solubilizers. We tested for residue and kept an eye on aquatic bugs. The bugs didn’t act any differently when sodium cumene sulfonate showed up in the water, compared to stretches where it didn’t. That doesn’t mean every stream everywhere can handle endless supplies, but the evidence points to this chemical breaking down fast enough for modern wastewater systems to keep up.
That said, concerns around “biodegradable” claims go deeper. Some companies slap the word on labels without showing any proof, muddying the waters for people who want to buy safer products. Truly sustainable products need to break down fully, without producing toxic leftovers along the way. Testing by independent labs and regulatory groups can reveal if a chemical really disappears in real-world conditions, not just in the lab. Until all brands publish this data, consumers can seek out products that share test results or certifications from groups that specialize in safer chemistry.
People can push for better ingredient transparency. It starts with reading labels, then reaching out to companies when chemistry looks fuzzy. Environmental groups also have a role to play, by advocating for tougher standards and clearer language. Some states and countries already ask for full breakdowns of chemical safety and fate—others lag behind.
Sodium cumene sulfonate, by most measures, breaks down well in the environment. That comes as good news for anyone worried about what swirls down the drain. Keeping an eye on independent studies, pushing for honest labels, and voting with your wallet can all help ensure that “biodegradable” keeps its meaning in the world of cleaning products.
Sodium cumene sulfonate shows up in more places than many people expect. It serves as a solubilizer and stabilizer in cleaning products, shampoos, and even liquid soaps. In my experience reading labels while shopping for household and personal care items, it almost always slips by unnoticed, often hiding under long chemical names. That sort of low profile sometimes leads people to assume it carries little risk, but skin contact tells a different story for some folks.
This compound falls under the surfactant group. Surfactants work by breaking up oils and dirt so water can wash them away. Sodium cumene sulfonate does a solid job in that regard, but it isn’t totally risk-free. Researchers and organizations like the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) panel have looked at its effect on the skin. Reports show it’s generally safe for the average adult at concentrations found in off-the-shelf products. Still, some people—especially those with sensitive skin—report irritation such as redness, itching, and even mild rashes after coming into contact with it. In rare cases, allergic reactions have been documented.
Parents of kids with eczema might already know how tricky it is to find soaps and shampoos that won’t trigger a skin flare-up. My own family has run into this issue with my youngest daughter, who can spot a harsh surfactant just by the way her skin feels after washing. Even though sodium cumene sulfonate isn’t the harshest chemical around, regular use can cause trouble over time for people with pre-existing skin conditions or allergies. Once, switching to a “gentle” labeled kid’s shampoo that still had this compound in the mix led to a week of dry, irritated patches on her scalp. It taught us to be more careful about ingredients that don’t always get much attention.
People trust that common soap ingredients won’t do them harm. Skin irritation might look like a minor inconvenience to some, but even a little rash can turn daily routines into an ordeal, especially for children or those with chronic skin conditions. Allergic reactions, though rare, can also become serious. Staying informed about what causes these issues lets shoppers avoid repeated discomfort and trips to the doctor. It also pressures manufacturers to reformulate for safety.
After dealing with a mild allergy scare in my own family, I started reading labels more carefully. Choosing products marked as “fragrance-free” or “for sensitive skin” often helps, though not always. Looking for transparent company websites and checking for independent safety certificates provides more confidence. For those already prone to skin problems, patch testing a new product can make a real difference—a small dab on the inside of the elbow spread out over 24 hours goes a long way in spotting an issue before it gets serious.
As awareness grows, some companies start moving away from surfactants like sodium cumene sulfonate, replacing them with milder alternatives. These options sometimes cost a little more, but for anyone coping with allergies or recurring irritation, that extra step of caution pays off in comfort. Doctors and dermatologists remain valuable sources for sorting out confusing ingredient lists and helping people identify which compounds trigger their symptoms.
Better ingredient transparency and stricter safety testing improve day-to-day life. Researchers keep looking for effective cleaning agents that clear safety hurdles for a wider range of skin types. Shoppers’ demand for safer, skin-friendly products has already influenced the personal care market, and that shift signals hope for anyone tired of guessing what causes their skin troubles.
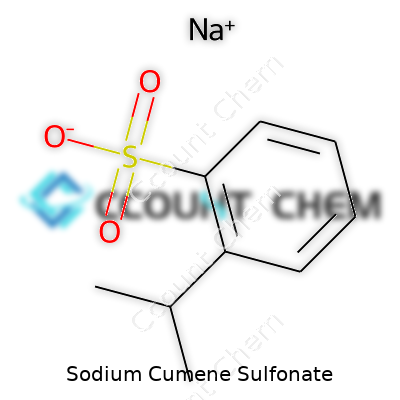
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | Sodium 2-(propan-2-yl)benzenesulfonate |
| Other names |
Sodium isopropylbenzene sulfonate Sodium cumenesulphonate Sodium 2-isopropylbenzenesulfonate Sodium isopropyltoluene sulfonate |
| Pronunciation | /ˈsəʊdiəm ˈkjuːmiːn sʌlˈfɒneɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | “28348-53-0” |
| Beilstein Reference | 3598733 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:9120 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1352 |
| ChemSpider | 9129 |
| DrugBank | DB11305 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.848 |
| EC Number | 205-055-6 |
| Gmelin Reference | 82120 |
| KEGG | C02626 |
| MeSH | D013002 |
| PubChem CID | 23665755 |
| RTECS number | GV8050000 |
| UNII | HLU1A85VKU |
| UN number | UN2581 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID0028572 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C9H11NaO3S |
| Molar mass | 272.35 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.05 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Freely soluble in water |
| log P | -2.3 |
| Vapor pressure | <1 mmHg (20°C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa ≈ -2.1 |
| Basicity (pKb) | >7 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -4.6×10⁻⁶ |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.485 |
| Viscosity | Viscosity: 15-40 cP (25°C) |
| Dipole moment | 4.6 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 262.7 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -726.6 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | A05XA53 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Causes serious eye irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS07, Warning, H315, H319, H335 |
| Pictograms | GHS07 |
| Signal word | No Signal Word |
| Hazard statements | May cause eye irritation. |
| Precautionary statements | Wash thoroughly after handling. Wear protective gloves/eye protection/face protection. If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-1-0 |
| Flash point | >100°C (212°F) |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 Oral Rat 1300 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral, Rat: 1300 mg/kg |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 0.5–6% |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Not established |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Cumene Cumene sulfonic acid Sodium p-toluenesulfonate Sodium naphthalene sulfonate |