Stories about chemicals often echo shifts in the scientific world, and camphorsulfonic acid shows just how much a simple molecule can turn into an industrial staple. Chemists in the early 20th century started playing with natural camphor, a fragrant molecule used in traditional remedies for centuries. Once sulfonation methods advanced, a new chapter opened up for camphor derivatives. Camphorsulfonic acid began gaining recognition as researchers figured out how its strong acid properties and chiral structure could support both synthesis and separation tasks in laboratories. Over time, what started as a curiosity for natural product chemists evolved into an indispensable reagent not just in research labs but also in pharmaceutical manufacturing and specialty chemical production. Its timeline stands as proof of how everyday needs—like purifying or making life-saving drugs—shape innovation and demand in the chemical world.
Camphorsulfonic acid consistently pops up in discussions about robust acids with a chiral twist. Chemists working in both research and industry circles know it as a white crystalline solid that dissolves well in water and many organic solvents. It acts as a strong organic acid, stronger than your average carboxylic acid, which lets it play in fields where traditional acids stumble. The compound’s chiral center brings unique value to asymmetric syntheses, letting it serve as a resolving agent when separating mirror-image molecules, especially in pharmaceuticals. This property doesn’t just mark camphorsulfonic acid as another entry in the many acetylenic or sulfonic acids cataloged over the years—it makes it a go-to choice when precision matters.
Anyone who has handled camphorsulfonic acid in a lab will remember its distinct, camphor-like odor and dense crystalline feel. The melting point often lies just above 190°C, and the acid boasts good stability under common storage conditions. Its solubility profile spreads out across a variety of polar and non-polar solvents, including methanol, ethanol, and acetone, making it a flexible ingredient in many synthetic applications. Under normal environmental conditions, the crystals resist decomposition, avoiding hygroscopic nightmares that plague some other acids. Its strong proton-donating ability comes from the sulfonic group attached to the camphor framework, delivering high reactivity in acid-catalyzed reactions. These physical features simplify storage, shipping, and handling, reducing risks and saving both time and money for industry stakeholders.
Clear technical data helps scientists avoid surprises, and camphorsulfonic acid rarely disappoints in this area. Purity standards for industrial bulk often reach upwards of 99%. The molecular formula weighs in at C10H16O4S, and the compound’s CAS number stays consistent across reputable suppliers for easier procurement and compliance checks. Labels on drums and bottles list hazard designations rooted in United Nations chemical transport codes, with attention paid to corrosivity, environmental warnings, and requirements for protective equipment. These details keep workers and supply chains informed, cutting down on missteps in storage rooms and shipment routes. Detailed documentation usually traces back to studies validating each lot for trace metals, residual solvents, and water content, ensuring peace of mind for any lab manager or plant operator.
The route to camphorsulfonic acid combines simple, elegant chemistry with precise controls, echoing the importance of process safety in modern plants. The journey starts with natural or synthetic camphor, which reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid or chlorosulfonic acid. The sulfonation proceeds smoothly under controlled temperatures and reaction times, guided by years of experience in scale-up chemistry. Once reaction endpoints are confirmed by standard titration or spectroscopy, products are neutralized, often extracted, then recrystallized to remove mineral acid residues and process impurities. Down the production line, filtration separates out the solid, followed by drying steps that consistently deliver the free-flowing crystalline powder seen in analytical and industrial lots. This hands-on sequence, informed by both tradition and continuous improvement, sets the baseline for quality and reliability in every batch.
The real utility of camphorsulfonic acid shows up when it kicks off or mediates reactions. Chemists use it as both a Brønsted acid and as a resolving agent to separate racemic mixtures—tasks critical to making single-enantiomer drugs. Through direct acid catalysis, it speeds up reactions such as esterifications and rearrangements without introducing water or other unwanted byproducts. Further, modifications to the camphor or sulfonic acid framework generate a variety of derivatives, including salts, esters, and complexes for more tailored applications. What stands out is its predictability; reactions with camphorsulfonic acid go by the book, making it a favorite among synthetic chemists looking for reproducibility and clean work-ups in both bench-scale experiments and full-scale reactors.
The nomenclature landscape can be a trap for the unwary. Chemists talk about (S)-(+)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid or CSA, and sometimes the older names still echo through procurement forms and textbooks—camphorsulfonic acid monohydrate, for example. Globally, trade and regulatory agencies demand precise name alignment, so documents and shipment manifests include unique identifiers like the InChI key and EC registry codes. Over the decades, these synonyms have built confidence and transparency into the supply chain, offering traceability whether the acid travels between academic labs, pharmaceutical manufacturers, or chemical distributors.
Strict safety routines keep labs and factories running smoothly, protecting both people and productivity. Camphorsulfonic acid, like many strong acids, brings corrosion risks, especially to metals and unprotected skin. Eye contact or inhalation can cause significant irritation, so proper gloves, goggles, and engineering controls become essential. Modern Material Safety Data Sheets outline emergency first aid, storage temperature limits, and compatible containers. Plants and research facilities routinely install proper ventilation, spill kits, and acid-resistant surfaces. New regulations, pushed by both local and international authorities, highlight the short- and long-term health effects, forcing organizations to adopt better training programs and personal protective equipment standards. This culture of caution doesn’t dampen innovation; instead, it helps scientists and operators trust in their tools and keep focused on results.
Ask around among chemists in pharma, and camphorsulfonic acid will top lists of essential reagents for making new drug molecules. Small-scale synthesis teams love its ability to drive chiral separations, speeding the path from discovery to candidate selection. In larger-scale production settings, its use extends to creating salts of active pharmaceutical ingredients, which can improve both stability and solubility—two huge hurdles during drug formulation. Beyond medicine, it plays a part in the synthesis of specialty polymers, catalysts, and even some flavors and fragrances. Its robust acid character shrugs off process impurities and keeps batch variability in check, making it a mainstay for anyone building complex molecules on schedule and within budget.
The race for new molecules never stops. Camphorsulfonic acid, with its unique combination of strength and chirality, keeps attracting researchers who want more selective ways to build novel pharmaceuticals and materials. Universities and private R&D labs around the world keep exploring its use for greener syntheses, using it to replace more hazardous or unmanageable acids. Publications keep emerging about tweaking its framework to create new derivatives with even punchier catalytic or resolving power. Partnerships with research consortia have led to the development of automated screening protocols, which has shortened drug discovery timelines and broadened the chemical space accessible to scientists.
Safety data has matured over decades of use, yet new questions always pop up as the regulatory climate tightens. Acute toxicity appears relatively low compared to heavier mineral acids, though ingestion and significant exposure remain risky. Chronic effects haven’t materialized in broad case studies, but inhalation of dust or repeated contact can sensitize skin and mucous membranes. Environmental specialists flag the need for careful disposal, since runoff or spills threaten aquatic habitats. Ongoing work by toxicologists aims to update exposure thresholds and refine medical guidelines, offering clearer pathways for safe work practices and environmental stewardship across the chemical industry.
The next era for camphorsulfonic acid looks promising. Demand for greener, more sustainable chemistry is driving new research into renewable sources and less energy-intensive production. Advances in chiral catalyst design keep camphorsulfonic acid relevant at the frontiers of innovation, especially as personalized medicine and custom molecules become the norm in pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals. Public concern around chemical safety and environmental impact pressures manufacturers and regulators to keep improving labeling, tracking, and waste management practices. What started as a niche acid built from a terpene now stands as a linchpin of modern chemical manufacturing, ready to meet new challenges as the world keeps raising the bar for effectiveness, safety, and sustainability.
Camphorsulfonic acid pops up most often in the world of synthetic chemistry. Step inside any organic chemistry lab, and you’ll find glass containers lined up with bottles of white crystalline powder labeled “CSA.” That’s the shorthand for camphorsulfonic acid, a compound prized for its strength as an acid without the risks tied to classics like sulfuric acid. Chemists, especially those making new medicines, rely on CSA to guide reactions that need a strong proton source but not the full brute force of corrosive acids. Patents for new treatments often mention CSA. Take, for example, the synthesis of new antihypertensive drugs. Active pharmaceutical ingredients can’t always handle harsh acid environments, so CSA gives that extra nudge without tearing up the molecular structure.
I’ve worked with research teams building molecules that don’t exist on store shelves. In fields like pharmaceutical R&D, developing a single pathway to a compound may cost millions. Adding a dash of camphorsulfonic acid often means the difference between a perfect yield and a total mess. Sometimes, reactions stall or churn out a nightmare of side products. CSA steps in—its sulfonic acid group performs well, then disappears when it should. For instance, making the antifungal drug fluconazole involved crucial steps where CSA had to protonate intermediates cleanly. Drug makers like using CSA because it rarely leaves behind gunky residues that slow down purification.
CSA doesn’t just hang out in chemistry textbooks. Factories rely on it to tweak the physical properties of ingredients. In the world of plastics, making certain materials flexible or pliable sometimes calls for a precise acid touch. Camphorsulfonic acid helps soften resins and adjust the viscosity of coatings. Some ink and paint makers also put it in their formulas to stabilize colors and keep mixtures even. It manages to do this without creating fumes, so workers in manufacturing plants face fewer hazards with CSA than with something like hydrochloric acid.
Electronics manufacturers have turned to CSA for doping organic polymers like polyaniline. These organic semiconductors process light or carry current, forming the heart of flexible screens and lightweight batteries. CSA helps transform those base polymers from weak conductors to materials ready for technical work. Researchers have documented cases where using CSA improved charge flow by several orders of magnitude, helping make electronics smaller and lighter.
As someone with a chemistry background, I’ve learned to respect even the “safe” acids. CSA won’t eat through gloves in seconds, but dust can hurt lungs, and long-term contact bothers skin. Companies have taken steps to improve worker safety. Splash shields, proper ventilation, and simple rules like “never add water to acid” come up during every onboarding. Laboratories switched to pre-measured packets, which cut mistakes and waste. CSA production has grown cleaner, with firms capturing byproducts and recycling solvents in a bid to limit the chemical burden on the environment.
Every chemical has a place, and CSA’s spot sits between brute force and precision. Chemists see it as a tool that opens new doors in medicine, electronics, and plastics. Regulations have nudged producers toward safer production and application. For anyone curious about what keeps the worlds of pharmaceuticals, clean energy, and flexible tech growing, camphorsulfonic acid is one of those quiet helpers that keeps progress on track without making a mess.
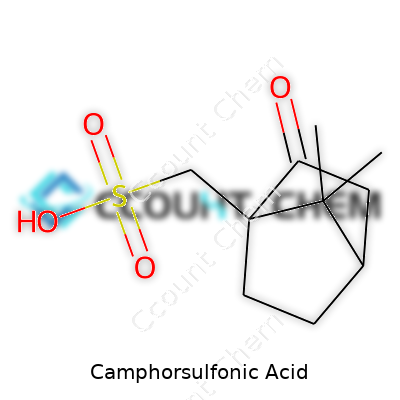
It’s easy to glance at a name like camphorsulfonic acid and picture a jumble of letters and science-lab mystery. The actual chemical formula is C10H16O4S, which draws a clear line from camphor, a substance smelling strongly of medicine cabinets and mothballs, to a powerful tool in chemistry. This single formula—ten carbons, sixteen hydrogens, four oxygens, and one sulfur atom—shapes a molecule that reaches well beyond textbook knowledge.
I’ve seen camphorsulfonic acid on shelves of both research labs and production facilities. Its main draw comes from its role as an acid catalyst, especially in organic synthesis. Chemists trust this compound to nudge reactions along without bringing water into the mix. For example, pharmaceutical companies use it to make life-saving medicines more efficiently. Stereochemistry—the way molecules orient in space—hinges on precise control, and camphorsulfonic acid steps in to provide that control.
People often think acids simply “burn” or “corrode,” but each one tells its own story. Camphorsulfonic acid belongs to a select group of strong, stable, solid acids that dissolve well in organic solvents. Compared to sulfuric acid, which chews through most surfaces, camphorsulfonic acid handles itself gently but effectively. That means workers can handle reactions with better control, less risk, and fewer side products.
The trust scientists put in this acid doesn’t come just from its formula; it comes from decades of safe, consistent results. Chemists rely on standard references, such as PubChem and Sigma-Aldrich, which confirm both the formula and the properties. Researchers refer to peer-reviewed articles (for example, synthesis techniques published in the Journal of Organic Chemistry) when evaluating new uses. Real evidence, not just anecdotes, shapes strong choices.
Camphorsulfonic acid might be “safer” than some alternatives, but it still deserves respect. Breathing the dust or getting it on your skin can cause harm, so gloves, goggles, and good ventilation aren’t just suggested—they’re necessary. Chemical knowledge means little unless it leads to safe work. I’ve seen teams in the lab leave open containers or neglect to clean up spills, only to deal with irritated skin or ruined samples. Proper handling always pays off—protecting both people and the end product.
A simple formula like C10H16O4S carries a surprising amount of weight. The blend of camphor’s solid backbone with the reactive sulfonic group brings both classic chemistry and practical results to the table. Knowing what’s actually in a compound, and respecting how it’s used, keeps science rooted in reality. That’s the real story behind camphorsulfonic acid—an ordinary-sounding chemical that has extraordinary reach, as long as folks treat it with the knowledge and respect it deserves.
People working with chemicals want the straight facts, not fear or fancy language. Camphorsulfonic acid, used a lot in pharmaceutical and organic chemistry labs, comes in as a white or sometimes off-white powder that bumps up reactivity and helps build all sorts of useful compounds. Many chemists—myself included—have handled this stuff. It pays to know what you’re working with.
Camphorsulfonic acid doesn’t top the charts for danger. I’ve seen much nastier acids in the lab. Still, this is a strong acid. Direct skin contact gives you irritation pretty fast. Eye exposure can sting badly and damage tissue—nobody wants to risk that. Inhaling its dust brings coughing, throat burn, and possible trouble breathing if a person isn't careful. Long sleeves, gloves, and goggles offer simple, effective protection. Most academic and industrial setups also have fume hoods or localized ventilation, and for good reason. These aren’t overkill precautions; they’re based on countless lab incidents and hard science.
Compared to strong mineral acids like sulfuric or hydrochloric, camphorsulfonic acid doesn’t corrode steel benches or burn through skin in seconds. Still, safety data sheets (SDS) list it as corrosive to eyes and skin with warning not to breathe the dust. If exposure does happen, the standard chemical hygiene routines work: rinsing skin or eyes, changing out of contaminated clothing, clearing the air. Data supports these steps as effective. Mistakes happen, even to old hands, so having a clear plan keeps a minor spill from turning into a big problem.
This acid doesn’t build up in the body and isn’t linked to chronic diseases like cancer. The biggest danger comes from mishandling. Acute exposure can bring burns and irritation, but you won’t see toxic effects from responsible use. Most environmental research shows it won’t stick around in soil or groundwater since it breaks down and dilutes quickly—much different than some heavy metals or persistent organic pollutants. Still, pouring any chemical down the drain isn’t a good look, and responsible waste management remains key in any lab or plant setting.
Chemicals like camphorsulfonic acid get a “dangerous” reputation based more on unfamiliarity than evidence. I’ve found that folks fresh out of school, or far away from the lab, lose their fear of acids once they learn how to handle them safely. The stories that stick with me involve someone rushing, skipping gloves, or working distracted. Training and respect for procedures prevent most issues, even when dealing with acids much stronger than camphorsulfonic.
Good habits do more for lab safety than any equipment. Gloves, eye protection, and proper storage block nearly every route of exposure. Training new staff is critical—mentorship in the lab beats any online module. Institutions and companies should support open reporting of accidents, too, since learning from mistakes builds a safer culture for everyone involved. Updated SDS sheets, regular audits, and equipment checks round out a solid safety plan. Treatment centers and first responders also benefit from knowing the handful of chemicals most likely to cause accidents in their area, and camphorsulfonic acid, while less common than some, fits that category.
Respect for camphorsulfonic acid goes a lot further than fear. Its hazards come from carelessness, not some hidden toxic trick. Good training, protective gear, and plain common sense keep people safe—whether in the world’s biggest lab or a small classroom. Sharing accurate, experience-based information beats myths and rumor any day.
Sulfonic acids like camphorsulfonic acid (CSA) bring useful properties into the lab. They help drive reactions in pharmaceuticals, electronics, and chemical research. Anyone who has worked in a busy lab, or even spent a few months mixing batches for R&D, quickly learns that these acids don’t forgive carelessness. News of an accidental spill or unexpected vapor can snap folks to attention. Skin burns and inhalation problems come up more often than you might guess. That’s why those clear, simple practices for storing CSA make the difference between a safe day at work and a costly accident.
Camphorsulfonic acid strongly absorbs water. I’ve seen jars ruined in just a few weeks because someone left a lid even partly ajar. The powder clumps, the label smudges, and then nobody trusts the quality. Best results come from using tight-sealing glass containers with screw caps. Polyethylene sometimes works in a pinch, but acid vapor eventually eats at plastics. Dry air storage cabinets help, especially in damp climates or during rainy seasons. Some chemists drop a silica gel packet right inside the jar for extra insurance. Humidity really cuts shelf life, no matter the expertise in synthesis or the planned experiment.
One lesson that sticks with me: don’t leave CSA anywhere near a hot water pipe or near a sunlit window. Heat ages the compound, and after repeated warming and cooling, clumps form that affect how much acid you actually measure out. Room temperature—steady, cool, and out of direct light—usually serves well. Aggressive refrigeration creates condensation in the jar, trading one problem for another unless there’s airtight protection. Storing on a low shelf away from heat sources works, but I always make sure no chemicals with clashing labels (like strong bases) sit nearby.
I’ve seen old reagent bottles without clear dates or names. Imagine trying to figure out if that off-white powder is what you think it is. One simple label—“Camphorsulfonic Acid, received 2024-05-12”—settles most doubts. Chemists working late shifts thank you. Auditors thank you. Label both the storage jar and, if split for a separate reaction, the working bottle. Date every container. For hazardous acids, chemical suppliers and safety agencies stress this step repeatedly. It’s not just for paperwork; it keeps people safe.
CSA doesn’t catch fire easily, but it reacts with bases or oxidizers if stored nearby. That’s where chemical compatibility charts save headaches. Some years ago, a neighboring bench at a university lab mixed acid fumes with ammonia stock—nobody wants that. Keep CSA in a chemical cabinet rated for acids, separated from alkalis and oxidizing agents. Use an acid-resistant spill tray under the jar. Standard ethanol-based disinfectants clean up most traces, but eye protection always goes on before handling clean-up for any acid, big or small.
Every team can boost safety with a few basic habits. Check your labels often. Wipe down moisture from tools before opening jars. Store acids and bases apart by several feet at least. Train new employees with real-life examples of spills and improper storage—these stories stick better than rules from a binder. Many chemical injuries never make the news, but everyone who has spent time at a lab bench knows the cost of ignoring these lessons. Good storage isn’t fancy, but it keeps people working, projects on schedule, and labs running well every day.
Camphorsulfonic acid, often labeled CSA in the lab, pops up all over organic synthesis for good reason. Having spent years working with it, I find that CSA combines accessibility, strength, and surprising selectivity. Researchers rely on it as a catalyst for reactions where other acids like hydrochloric or sulfuric just steamroll their way through sensitive molecules. CSA’s structure and solid form make it just plain easy to weigh out—no sticky liquids, no sharp fumes, fewer worries about accidental spills and corrosion.
Pharmaceutical chemists often reach for CSA during chiral resolution. Many drugs, from beta blockers to antiviral agents, need a high enantiomeric purity since the “wrong” mirror image can be useless or even harmful. CSA comes in both enantiomeric forms. It teams up well with racemic bases (especially alkaloids and amine-containing drugs) to pull apart the left-handed from the right-handed molecules. The resulting salts offer a practical path to purer, safer compounds. I’ve watched as whole batches of intermediates get transformed, and when I run optical rotations later, the difference jumps right out in the numbers.
Lab routines sometimes feel repetitive, but acetalization rarely fails to surprise. Protective groups shield alcohols or carbonyls from states they would regret: heat, strong bases, harsh reductions. CSA really shines here. Instead of bullying the reaction, it nudges it. With just a catalytic dusting, CSA triggers acetal and ketal formation, and it leaves sensitive functional groups less battered than after mineral acids. When students ask how to keep their product clean, I show them a CSA-catalyzed rundown – the TLC plates look like magic.
Certain transformations, especially those involving rearrangements or the creation of new rings, rely hard on proton sources tough enough to generate carbocations but soft on fragile aromatics. CSA consistently produces these intermediates without chewing up precious starting material. Fragrance chemistry draws on this advantage all the time, since terpenes and related compounds hate rough conditions.
Large-scale peptide manufacturers have always cared about efficient protecting group removal. Small research teams rely on the same approach. CSA effortlessly knocks off tert-butyl based protecting groups, letting the main chain stay intact. Working with CSA, I saw dozens of crude peptides clean up without a sea of side products. In a market where synthesis time often means the difference between competing drugs, that reliability matters.
CSA’s solubility in water and alcohols pays off during workups. After a reaction, I just filter and wash, skipping the harsh neutralizations that leave behind mountains of salt waste. As labs push for cleaner, safer, and less wasteful protocols, CSA looks better and better. The rise in green chemistry efforts means acids with low toxicity and minimal environmental impact attract more attention—and CSA fits right in.
Whether a chemist works in flavor research, medical compounds, or new materials, chances are camphorsulfonic acid helps shape a few critical steps. The compound bridges the lab’s practical side and the goals of safe, pure, and cost-effective molecular assembly. CSA delivers a blend of selectivity and convenience worth paying attention to. Its solid form, strong yet gentle nature, and history of dependable performance keep it relevant in laboratories committed to high-quality outcomes.
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | (1R,4R)-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl sulfonic acid |
| Other names |
10-Camphorsulfonic acid CSA Camphor-10-sulfonic acid Kampsulfonic acid 1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl hydrogen sulfate |
| Pronunciation | /ˌkæm.fɔːr.sʌlˈfɒn.ɪk ˈæs.ɪd/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 5872-08-2 |
| Beilstein Reference | 3590348 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:35649 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL113709 |
| ChemSpider | 57404 |
| DrugBank | DB14624 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.281 |
| EC Number | 207-179-9 |
| Gmelin Reference | 55466 |
| KEGG | C01015 |
| MeSH | D002193 |
| PubChem CID | 9147 |
| RTECS number | GV7875000 |
| UNII | R32DQT1Q2X |
| UN number | UN2585 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H16O4S |
| Molar mass | 232.29 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.346 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| log P | -2.2 |
| Vapor pressure | < 0.01 mm Hg (20°C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | -1.2 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 1.4 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -64.0·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.558 |
| Viscosity | Viscous liquid |
| Dipole moment | 6.44 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 309.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | A01AB16 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Causes severe skin burns and eye damage. Harmful if swallowed. Harmful if inhaled. |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS05, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS05,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H302, H314 |
| Precautionary statements | Precautionary statements: "P280, P305+P351+P338, P310, P264, P301+P330+P331 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 3-1-2-W |
| Flash point | 92 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 280 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 oral rat 2000 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Rat oral 2500 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | GR7875000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 1.00 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Camphoric acid Camphor Sulfanilic acid p-Toluenesulfonic acid |