Chemists in the late 19th and early 20th centuries sought novel compounds to drive the rapidly evolving dye industry. This search led to the emergence of sulfonated aromatic amines. Over time, advances in sulfonation and nitration brought 3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid into focus. Lab notebooks from the early chemical manufacturers show how research teams, drawing on methods like diazotization and careful sulfonic acid substitutions, shaped the groundwork for how this molecule would be produced on an industrial scale. Each refinement marked a new chapter in colorants and intermediates, as factories moved away from crude natural dyes in favor of more reliable synthetics that performed well under harsh laundry and sunlight conditions. I recall from reading old journals that the shift from reliance on cumbersome imported pigments to locally synthesized aromatic sulfonic acids was genuinely transformative for textile makers.
Today, this compound sits among the most sought-after nitroaniline sulfonic acid derivatives, valued for its role in azo dye synthesis and specialty pigments. Unlike broad-use raw materials, this molecule finds a home in more targeted segments, such as the development of reactive dyes suited for wool, nylon, and silk. Firms in the colorant market recognize its distinct molecular signature—which brings an amino, a hydroxy, and a nitro group onto a single aromatic ring—as providing both chromatic intensity and versatility. Chemists pinpoint it as a solid intermediate, meaning it forms a backbone for more complex molecules yet offers enough functionality for standalone uses in technical applications.
You’d recognize 3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid as a yellow-to-brownish crystalline solid, water-soluble due to the sulfonic acid group, with a mildly acidic to neutral pH in solution. Its molecular formula, C6H6N2O6S, doesn’t suggest volatility or the dangers associated with many volatile aromatics. From the bench, I can tell this compound steadily dissolves in warm water, giving an orange-tinged solution that is stable through a broad pH range. Its melting point sits well above ambient temperatures, supporting straightforward storage out of direct sunlight. Chemically, the presence of both nitro and amino groups allows for redox activity and easy participation in azo coupling reactions. The sulfonic moiety lends stability, increasing utility in aqueous processes where simpler nitroanilines would drop out of solution.
Producers ship this compound under rigorous labeling protocols covering purity, molecular mass, solubility, and permissible contaminants. Authentic samples meet minimum thresholds for assay—generally above 98%—and have tightly controlled levels of heavy metals, iron, and chlorides, which can otherwise disrupt downstream dye syntheses. The devil’s in the details: slight contamination with metals or residual acids noticeably dulls the sharp colors in finished dyes. My own experience in quality assurance labs highlighted the need to monitor lot-to-lot consistency, not just for regulatory compliance but to guarantee reproducible performance in customer applications. Labels always specify handling hazards, personal protective equipment requirements, and compatibility instructions to prevent cross-contamination.
Preparation generally unfolds in two main steps—sulfonation and nitration, followed by amination or, less frequently, hydrolysis of a protected intermediate. Industrial chemists, aiming for bulk yields, prefer direct sulfonation of nitroaniline or interconnected multi-step reactions to minimize side products. Temperature, acid concentration, and reaction time drive the efficiency of each transformation, with post-reaction neutralization and filtration concentrating the product. Factory setups invest considerable effort in waste acid recovery, reducing both environmental impact and production costs. In academic labs, smaller-scale routes employ milder reagents but mirror the industrial principles: controlled addition, vigilant temperature management, and careful crystallization. My experience with pilot runs demonstrated that yield optimization often hinges on the purity of the starting nitroaniline and the precision of sulfonic acid addition, underscoring the value of in-process monitoring.
3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid thrives in coupling reactions, especially when it acts as a diazo component for azo dye manufacture. It can react directly with diazonium salts under mild conditions, forming intense, fast dyes suitable for technical textiles and industrial coatings. The nitro group offers a portal to reductive transformations; catalytic hydrogenation gives rise to derivatives that serve as intermediates for specialty pharmaceuticals and advanced pigments. Sulfonic acid derivatives participate in metal complex formation, broadening the scope for advanced materials. My years spent troubleshooting plant-scale reactions taught me that even subtle variations in pH or reagent freshness could shift the product profile, making real-world expertise as crucial as textbook chemistry.
Within trade circles, 3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid moves under a collection of synonyms such as Fast Acid Brilliant Yellow 10G Acid, m-Amino-p-nitrophenol-5-sulfonic acid, and various manufacturer-specific codes like “Acid Yellow Base C.” These names can trip up even experienced buyers. I’ve often seen component mismatches on purchase orders simply due to overlapping product numbers across catalogs, underscoring the importance of cross-referencing CAS numbers and in-house identifier lists for effective risk management.
Safe handling depends on good ventilation, skin protection, and strict separation from incompatible oxidizers or reducing agents. The presence of a nitro group introduces some risk under conditions where reducing agents stray into process lines, and dust must be minimized. Long-term storage prefers cool, dry rooms with clean labeling and outdoor access in the case of bulk-scale production. Industrial standards lean on GHS labeling, data sheets, and annual refresher training for workers. In the lab, attention to basic respiratory and dermal protection pays dividends, as accidents involving aromatic sulfonic acids—though rare—require laborious cleanup and detailed medical follow-up. I’ve seen how operational lapses, often small, lead to process disruptions and, far more importantly, to health scares.
Textile dye makers employ this chemical in substantial volumes for direct and reactive dye synthesis, particularly in wool and synthetic blends. Water treatment companies value its sulfonic acid character for designing specialty resins and sensors. Chromatographers sometimes use the molecule as a reference marker and, more recently, in separation media development. A research colleague once explained how they used similar sulfonic mixtures to fine-tune pigment stability in inkjet printers, appreciating this compound for its resistance to fading and bleeding, which traditional dyes couldn’t match. Specialty pigment manufacturers exploit the consistent hue and fastness attributes, feeding growing demand in sports apparel, automotive finishings, and anti-corrosive coatings.
Research doesn’t rest. Teams in both academic and private sectors push to expand the application envelope for this compound, looking to design next-generation UV-fast dyes and environment-safe pigment processes. Studies into greener synthesis routes, using less harsh sulfonating or nitrating agents, promise to lower both emissions and raw material costs. The move to digital textiles hinges partly on better dye intermediates, which is driving an uptick in patents covering both preparation methods and unique derivatives. In my contacts with R&D labs, a recurring message is that incremental tweaks—a more selective catalyst, a modified sulfonic group—unlock surprising advances in color vibrancy and wastewater clean-up.
Studies examining this compound’s toxicological profile remain ongoing. Acute exposures appear to carry moderate risks, with routes including skin contact or inhalation during bulk transfer. Chronic effects from long-term, low-dose exposure receive careful screening, under tightly monitored animal trials and in vitro cell studies. The nitro group, while contributing valuable functionality, brings heightened scrutiny due to its metabolic breakdown products, some of which show low-level mutagenicity in early screening. Wastewater analysis proves essential for compliance, with authorities demanding thorough tracking of residuals in effluent streams. From past involvement in regulatory audits, I can say that a comprehensive workplace monitoring program—not just periodic air sampling—complements ongoing toxicity reviews to support both individual safety and broader environmental standards.
Emerging trends point to further modifications of this molecule for expanded functionality in technical colorants, smart polymeric materials, and analytical sensors. Efforts intensify around low-chemical environmental processing, including catalytic conversion and microbial remediation to contain both product and waste footprints. Industry clients press for even sharper color yields with less dye usage, placing pressure on R&D to tune every aspect of this intermediate for cost and sustainability. Regulatory projections forecast tighter limits on industrial byproducts, prompting suppliers to overhaul synthetic lines and develop eco-tuned variants. My reading of patent filings and new product launches makes it clear that whoever cracks the durable, safe, and environmentally friendly colorant could reshape markets well beyond textiles, expanding this compound’s relevance in ways yet to be fully realized.
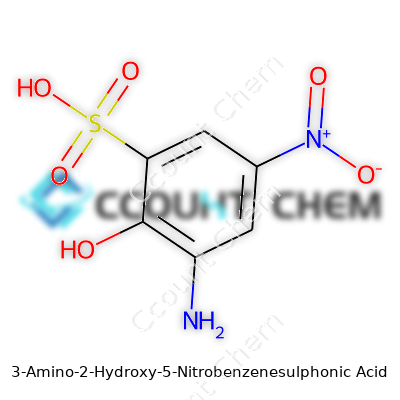
3-Amino-2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzenesulphonic acid brings together a tangled web of functional groups with uses in organic chemistry and dye sciences. Its chemical formula is C6H6N2O6S. This formula reflects a benzene ring rigged with an amino group at position three, a hydroxy group at position two, a nitro group at position five, and a sulfonic acid group anchoring it off the ring. Each atom in this arrangement impacts how the molecule behaves, from its solubility right down to how it binds during chemical reactions.
This compound stands out because it brings so many different functional groups to the same table. The amino group gives the whole molecule a way to interact in reactions that call for nitrogen. The hydroxy group boosts its solubility in water and adds another dimension for making connections in synthesis. The nitro group, notorious for adding electron-withdrawing heft, makes the molecule a good candidate for processes where reactivity shifts in the ring matter. The sulfonic acid group hands over water solubility and allows the acid to easily dissolve and disperse—crucial in industrial dyeing and chemical manufacturing.
I first came across this compound in an industrial dyes lab, staring at buckets of powder destined for use in textiles. It’s heavily used as an intermediate in the production of azo dyes. This field has relied on such compounds since the late 1800s to brighten up fabrics from everyday shirts to flags and uniforms. Back then, textile factories paid good attention to how quickly dyes would wash out or fade, and this acid gave a nudge toward longer-lasting color thanks to its interaction with various fibers and mordants.
Beyond the dye pot, chemists value it in the synthesis of more complex molecules in pharmaceuticals and laboratory reagents. The groups attached to the benzene backbone make it versatile—a starting point for reactions and an intermediate for much bigger, more valuable compounds.
With all these groups in play, anyone handling this chemical should respect its potential hazards. Nitro and sulfonic acid groups can both irritate skin and airways, and spills mean environmental trouble where waterways meet industrial discharge. Not enough attention goes into properly removing dye intermediates from waste streams, and old habits of dumping run-offs still linger in parts of the world moving fast to industrialize. In my experience working in older facilities, chemists and workers sometimes took shortcuts with waste, unaware of long-term consequences.
Regulation has tightened over the years. Factories now face strict controls on chemical handling, wastewater treatment, and reporting. Preventing damage starts with active education—workers need to know what they handle and why safe disposal matters. Using modern filtration systems and closed-loop processing, manufacturers can sharply reduce pollution, but it takes commitment, consistent investment, and a willingness to prioritize environmental health over short-term gain.
Companies eager to be responsible have started to review the full life cycle of their compounds. Cleaner production techniques, investment in research to find less hazardous intermediates, and better public information all become part of the puzzle. As consumers wake up to the story behind what colors their clothing, industries face a call to transparency. Providing clear labeling and traceability down to the intermediate chemicals used can help buyers make better choices and encourage manufacturers to act with care.
3-Amino-2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzenesulphonic acid may look like another mouthful out of chemistry class, but ask anyone with an eye for color or an interest in public health, and it’s clear: every atom in that formula counts, both for the science and for the people downstream.
Factories, power plants, and small workshops rely on this product to keep their machines running. Take the energy sector, for example. Every day, power generation relies on stable reactions, predictable performance, and reliable supply. Just about every engineer I know in the field talks about how reliability trumps everything else, and having material they can trust makes their jobs a lot more straightforward. Problems with product purity or supply disruptions create headaches that ripple out from control rooms to customers.
Hospitals and clinics depend on high-purity ingredients to make medicines. Think about pain relievers, antibiotics, and even vitamins—substances people reach for without a second thought. Pharmaceutical makers choose products that already meet the highest quality checks. If the base ingredients change from batch to batch, any mistakes show up fast, sometimes risking patient safety. My own family has seen the difference reliable medicine makes during times of illness. Consistent product safety means peace of mind for doctors and patients.
In the countryside, fields stretch out for miles, with crops relying on fertilizers for growth. Fertilizer blends with trace elements from reliable sources help farmers feed more people using less land. This efficiency matters everywhere, but in drought-prone or poor soil regions, it changes lives. Talking to farmers, I hear stories every season about crop challenges, but using a known fertilizer formula helps steady their planning. Mistakes in the mix show in lost harvests and tighter budgets.
Walk into a supermarket, and you’ll find cleaning products, food packaging, and personal care items that started with base materials of this type. For example, detergents clean better with stable chemical building blocks. Food wrappers need to be safe for families. Consistency matters here, too. The last thing any brand wants is a recall over tainted or faulty packaging. As a parent, it’s tough to imagine risking a child’s well-being over shortcuts in the ingredient list.
Tech companies use this product to make batteries, screens, and small sensors. Clean manufacturing and predictable quality help inventors bring new gadgets to market. Whether building thin batteries for electric vehicles or tiny chips for smart devices, tech workers depend on each shipment to behave as promised. Charging a new phone or electric car should be worry-free, thanks in part to these background materials doing their job. The push for clean energy and faster gadgets means demand keeps rising, with little room for error.
Right now, the focus should land on strengthening supply chains and setting higher safety standards. Calls for more rigorous testing and clearer tracking of ingredients come up in news and industry meetings. Factories need tools and staff who spot problems before they hit the shelves. Regulators want easier ways to trace products back to their source. Open communication between producers, users, and inspectors keeps everyone safer and more prepared for future needs.
3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid finds its way into dye and pharmaceutical labs, often ending up stored at the back of a chemical shelf. Its structure brings together a mix of groups that can react with the air, light, and water around them. I remember the first time I handled this material, one rule stood out during the safety training: moisture is the enemy. Letting it soak up water from the air changes the game, making your next step unpredictable.
Once the container’s seal breaks, the powder draws in water like a sponge. That clumping not only messes with precise weighing, it can trigger slow, quiet changes in the chemical. These changes sneak up on you — results look off, waste goes up, and so does the risk for a messy reaction. I’ve seen this happen in more than one lab, and I’ve cleaned up the sticky, stained glassware.
To dodge these headaches, chemical companies supply this acid in tightly sealed containers. Folks who understand this make sure to transfer it quickly and close the lid fast afterward. Some go further and keep desiccants in the storage cabinet to pull stray moisture out of the air. I keep silica gel packs handy for just this reason, having learned the hard way how much time a simple oversight can waste.
This compound isn’t explosive, but it doesn’t take much to cause skin or eye irritation. Sulfonated aromatics often slip onto the skin and leave stubborn stains. Gloves, eye protection, and a well-ventilated space become part of the daily routine. Safety data sheets recommend splash goggles and no open food or drink in the area. Simple steps, but one lapse can turn into days of discomfort or long hours scrubbing colored streaks from your hands.
Accidents do happen. Someone will drop a spatula or spill a few grams. I’ve learned that it pays to have an emergency cleanup kit—spills stay easier to handle if you act fast with an inert absorbent. Trying to wash the mess away with water just spreads the color and smell. Shoveling the powder with a clean scraper, then wiping surfaces with damp towels folded over several times, minimizes residues.
Heat nudges this acid to break down faster. Leaving it near steam pipes or sunny benches means the bottle won’t last as long, and impurities show up quicker. I keep sensitive chemicals below 25°C, and in some hot climates, this means a spot in a temperature-controlled cabinet. Always check that storage is away from direct sunlight and not next to a window, even in winter.
The bright colors and water solubility trick people into rinsing leftovers down the drain. This invites environmental risks. The right move is to collect waste into a designated container for hazardous organic chemicals. Most universities and companies arrange for professional disposal, but I always get people talking upfront about their plan for leftovers. Getting this right shows respect for local regulations and the community around the lab.
Careful labeling makes a difference too. Too many times, old bottles collect dust with unclear or faded labels, leading to confusion months later. Keeping dates, purpose, and full chemical names on every bottle stops most mistakes before they start. Training new team members on these details—how to scoop the powder, reseal containers, and spot signs of contamination—saves real trouble down the line.
To sum up, experience teaches that 3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid offers few second chances if mishandled. A dry cupboard, steady temperatures, clear labels, and a no-nonsense approach to spills give everyone in the lab a safer shot at their work.
Most folks won’t see 3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid in the grocery aisle, but those who spend time working in labs, in dye manufacturing, or in the textile world might know this yellowish powder. Its story isn’t just about chemistry. It’s about whether or not people should worry about this mouthful of a chemical around their work, their water, or their families.
You’ll mostly find this acid involved in making dyes and pigments. Textile industries and paper production rely on it to bring out colors that last. Pop it into the mix, and shirts, tents, packaging, and all sorts of printed materials show brighter blues, reds, and oranges. Chemists turn to it for reactions that don’t work well with other substances. From personal experience, just opening a container releases a distinct, acidic smell that lingers on your hands long after washing.
The first question from anyone who spends more than a few minutes with industrial chemicals is simple: Will it hurt me? Plenty of research points to definite risks. 3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid doesn’t belong on the dinner table or near your skin without protection. Inhalation can lead to coughing, nose irritation, and sometimes headaches. If it touches skin, rashes or redness can show up—nothing to brush off lightly. Years ago, a colleague ended up with a nasty rash after accidentally spilling a dilute solution on his arm, even though it seemed harmless at the time.
Research, including safety data from the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), confirms this acid may cause serious eye irritation. Swallowing it by accident could mean stomach pain or even worse outcomes; animal studies link it to liver and kidney effects in high doses. Toxicity to aquatic life also stands out, so careless dumping or leaks can have ripple effects on rivers and fish. Factories handling drums of it need proper drainage and waste systems to keep the chemical out of the local water table.
Simple rules matter the most. Protective gloves, safety glasses, and fume hoods should be the baseline. At work, Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) hang on the wall for a reason. Every workplace accident I’ve witnessed started with someone ignoring basics like ventilation or personal protective gear. No one expects emergency showers or eye-wash stations to get used, but they’ve saved more than a few folks from a dangerous mistake.
Safe storage cuts down the risk of accidental mixing or spills. Containers need tight seals, clear labels, and a spot away from sunlight or heat that might set off strange reactions. Regular checks aren’t only for the checklist—they catch the slow leaks and stains that lead to big issues down the road. My time on a factory floor taught me that prevention beats any cleaning job.
Plenty of companies search for less hazardous chemicals to replace traditional dye ingredients. Research on plant-based colorants and safer synthetic alternatives continues, but specialty dyes still lean on these nitrobenzenes for their staying power and color range.
If more industries pushed for safer substitutes, older compounds could fade out. Until then, everyone handling this acid needs to know what’s in front of them, stay informed, and treat it with the respect dangerous chemicals demand. The facts are clear—trusting luck over good habits never ends well around strong acids and dyes.
A lot of folks working with chemicals or unknown products have asked me, "Can you provide the material safety data sheet for this product?" I get where that comes from. MSDS means safety. Whether you work behind a hardware counter, in a science lab, or keep a maintenance closet at school, you want to know what’s in the bottle. Sometimes the smell isn’t enough for peace of mind. Sometimes you need a piece of paper that lists numbers, warnings, emergency procedures, and tells you exactly how harsh or risky the contents really are.
This need didn’t grow overnight. Incidents like the chemical plant disaster in Bhopal, India, and lead paint in children’s toys led to rules. The US Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) began pressing employers in the 1980s to keep these data sheets on hand. Europe built its REACH regulation and the safety card came right along. Because someone in the past skipped proper labeling or training, lives changed forever.
I’ve looked through hundreds of these sheets. They almost always have essentials, like the product’s common name, ingredients, physical details, storage needs, and firefighting measures. The best ones explain first aid – what to do if someone swallows it, breathes it, gets it on their skin, or splashes it in their eyes. You’ll usually see advice on cleaning up spills, safe disposal, and how to store the product away from things it might explode or react with. It ends up being a roadmap for people who work with the product every day, not just a legal document.
Some companies treat MSDS requests almost as a bother. That sends the wrong message. If a supplier dodges your request, that should set off alarms. Easy MSDS access shows the maker cares about you and the environment. I trust a supplier who posts these on their website, up to date and easy to find. The move toward SDS (Safety Data Sheets), which follow a worldwide standard, helped even more. SDS puts information in the same place every time. OSHA started requiring employers to train staff on these sheets each year. It’s not just paperwork; it keeps workers out of the ER.
People still run into trouble getting these sheets. Imported goods sometimes show up with incomplete paperwork or poorly translated warnings. Local suppliers may drop the ball, especially for older products that rarely sell. Old-style MSDSs can hide details in jargon. Some small businesses don’t store digital files and only print them when asked.
One effective fix: build an online, searchable database. Plenty of my former workplaces now use cloud-based systems, often free. Even a simple Google Drive folder, maintained by the safety officer, gives everyone access. Store managers or head custodians should check that all products, new and old, have sheets. If a sheet looks outdated or hard to read, chase the supplier. Regulations give you that right. Industry leaders have begun using QR codes on product labels that instantly link to updated sheets. This takes guesswork and delay off the table.
People sometimes roll their eyes at “safety paperwork.” Until something spills or gets in someone’s lungs, eyes, or mouth. I once watched a colleague avoid a trip to urgent care because we found the antidote steps in the MSDS. That piece of paper gave us clear instructions when no one remembered the product’s secret hazards. No lecture or yearly training replaces the power of having that information at your fingertips.
Access to a complete and honest sheet isn’t about ticking boxes. It honors the health of workers and their families, respects the local fire crew, and keeps the land or water supply from contamination. Every time someone asks for an MSDS and gets it, that’s a small act of prevention and respect. That’s the kind of safety culture that matters—for everyone.

| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 3-amino-5-nitro-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid |
| Other names |
5-Nitro-m-amidol 5-Nitro-3-amino-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid 5-Nitro-1-amino-2-hydroxy-4-benzenesulfonic acid |
| Pronunciation | /ˈθriː əˈmiːnoʊ tuː haɪˈdrɒksi faɪv ˈnaɪtroʊ bɛnˈziːnˌsʌlˈfɒnɪk ˈæsɪd/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | [96-27-5] |
| 3D model (JSmol) | `3D model (JSmol)` string for **3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid** is: ``` Nc1cc(S(=O)(=O)O)cc([N+](=O)[O-])c1O ``` This is the **SMILES** string, which JSmol and other molecule viewers utilize to render the 3D structure. |
| Beilstein Reference | 1940713 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:135175 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL42808 |
| ChemSpider | 14642017 |
| DrugBank | DB16875 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03c1d7b7-661d-42a6-bd47-c1a1c97c7cec |
| Gmelin Reference | 75453 |
| KEGG | C14801 |
| MeSH | D017360 |
| PubChem CID | 11472 |
| RTECS number | SW6300000 |
| UNII | S099W83474 |
| UN number | UN3439 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | 3-Amino-2-Hydroxy-5-Nitrobenzenesulphonic Acid CompTox Dashboard: "DTXSID0049754 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H6N2O6S |
| Molar mass | 232.17 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.87 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Soluble in water |
| log P | -2.5 |
| Vapor pressure | 3.3 x 10^-7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.3 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 6.66 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -53.8·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.651 |
| Viscosity | Viscous liquid |
| Dipole moment | 6.98 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 235.6 J K⁻¹ mol⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -416.0 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -1222 kJ·mol⁻¹ |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if swallowed. Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS07, GHS09 |
| Pictograms | GHS07,GHS09 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 2-1-1 |
| Flash point | > 220 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 (oral, rat): > 2000 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): >2000 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| NIOSH | SW7700000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 0.02 mg/m3 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
2-Amino-5-nitrophenol 3-Amino-4-nitrophenol 3-Amino-4-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid 4-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid 2-Hydroxy-5-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid 3-Amino-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid |