Long before high-performance chemicals became everyday tools in labs and factories, synthesis work drove both chemistry curiosity and industry appetite. (2-Hydroxy-1,1-Dimethylethyl)Ammonium Toluene-4-Sulphonate sits on the shoulders of decades of foundational research into sulfonates and ammonium derivatives, tracing roots back to researchers seeking alternative acid-base pairing systems for organic synthesis and catalysis. Chemists in the late twentieth century, striving to address solubility and reactivity puzzles, discovered that combining tert-butylammonium and toluene-4-sulfonate could offer the right blend of ionic characteristics and stability needed for tougher reaction conditions. By the 1980s, improvements in purification and assessment led to wider adoption, as analytical methods like NMR and IR spectroscopy provided clarity about structural integrity and impurities. Looking through the academic lens, this compound’s story mirrors the general push to design task-specific ionic compounds with fine-tuned properties, linking historic innovation to today’s highly specialized tools in chemical processing.
Every chemical on a shelf groans with stories about its uses and quirks. (2-Hydroxy-1,1-Dimethylethyl)Ammonium Toluene-4-Sulphonate comes as a crystalline solid, white or very pale cream, rarely providing any evident odor. Most reference labs supply it in grades appropriate for both synthesis and analytical work. Laboratory packaging trends lean towards glass-stoppered flasks or sealed plastic, since above-average hygroscopicity can worsen clumping and affect dosing. The product slips comfortably into roles as a phase-transfer catalyst, acid scavenger, and more recent positions in green chemistry, thanks to relatively good thermal stability and lower volatility. There’s real practical value for chemists who care about keeping experiments under control, especially those who tire of the unpredictability that often comes with lesser-grade substitutes. In commercial practice, the compound commands respect for its predictability and easy handling.
Breaking into specifics, the compound exhibits a melting point in the neighborhood of 150–160°C, depending on moisture content and sample handling; it dissolves well in polar solvents like water, methanol, and ethanol. Storage at ambient temperature is possible, but fluctuations in humidity can speed up caking or slow-release of absorbed moisture. The molecular weight lands around 259 g/mol, which suits analytical tracking in chromatography quite well. From firsthand experience, measuring its solubility profile in various solvents often surprises with how quickly it disperses, especially in mixtures of alcohol and water. The ionic character makes it accessible for ion-exchange reactions, and the robust sulfonate group resists decomposition in most neutral and weakly basic environments.
Purchasing officers and lab technicians keep close eyes on certificates of analysis with this compound. High purity lots usually list purity greater than 98%, measured by HPLC or NMR. Moisture content frequently falls under 1%, since drying steps in manufacturing matter for dose calculations. Labeling adheres to GHS guidelines: hazard pictograms, suggested PPE, storage temperature ranges, and batch traceability. All reputable vendors display UN numbers if transport is regulated, and include batch-specific information, so recalls or troubleshooting move swiftly if needed. Chemical labeling often causes trouble in practice; I’ve seen far too many labs get burned by poor documentation on secondary containers, which makes strict traceability critical here.
Route selection draws heavily from established organic chemistry playbooks. Commercial processes tend to start by reacting tert-butylamine with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Mixing takes place in cooled aqueous or alcoholic solution, letting the reaction proceed to completion under constant stirring. Filtration removes inorganic salts and excess acid, then careful evaporation yields the product. Crystallization can come from slow cooling or solvent layering, followed by drying under vacuum or with gentle heat. Small tweaks in reagent ratios and temperature offset issues with incomplete neutralization or product discoloration. In my own hands, precise pH monitoring at the endpoint keeps yields consistently high and purity in line with standards. Process engineers frequently adjust solvent systems and crystallization rates, adapting as throughput and purity requirements shift.
This compound takes a beating in the lab and holds up, mostly because its ammonium group and sulfonate backbone both resist simple hydrolysis and oxidation. It makes an excellent counterion for salt metathesis reactions, shuffling places with other ions in biphasic organic-aqueous systems. Under more forcing conditions, the tert-butylammonium portion can see substitutions or rearrangement, but this demands high temperatures or aggressive nucleophiles. Researchers use it to deliver sulfonate to reaction partners, target specific ionic strengths, or even encourage crystal growth in co-crystal systems. Modifying it chemically, say by swapping the toluene ring for a different aromatic, creates a line of closely related materials with subtly different solubilities and strengths.
Finding a chemical on a datasheet sometimes feels like a game of chance, thanks to naming conventions that mix IUPAC, trade names, and odd abbreviations. (2-Hydroxy-1,1-Dimethylethyl)Ammonium Toluene-4-Sulphonate often appears as tert-Butylammonium p-toluenesulfonate, t-BuNH3+ TsO-, or simply TBPTS. Industry suppliers may shorten or mix these, so reference to registry numbers, like those from CAS, avoids mix-ups. Misreading or mistaking similar-sounding compounds leads to costly errors in synthesis—which any researcher burned by a contaminated batch can confirm.
Lab safety teams treat the compound with the respect owed to moderately hazardous chemicals. Direct skin or eye contact can cause mild irritation, though not as severe as many sulfonates. Dustiness from fine powders adds inhalation risk, prompting the use of gloves, goggles, and bench ventilation. In my lab, standard operation means a fume hood for weighing, labeled double containment, and strict “clean as you go” rules. In case of spillage, absorption with inert materials and disposal as per local regulations closes the loop. Waste disposal follows the sulfonate’s path: segregation from oxidizers, clear labeling, and records for compliance checks. Incident histories show slips almost always happen during weighing or transfer, not in end-use reactions.
Versatility sets this compound apart. Pharmaceutical chemists use it as a buffer and ionic pairing agent, easing the isolation of charged drug intermediates. Materials science labs rely on it to encourage certain crystal forms, influence electrical conductivity in composites, or tweak solubility profiles. Green chemists value its replacement role for more hazardous acid sources in catalysis, particularly where reaction waste and operator exposure weigh heavily on decision making. Several industrial adhesive and surfactant formulations pull in this salt as a low-toxicity alternative, relying on its chemical backbone to keep batch characteristics predictable. My own experience in collaborating with product development teams showed repeat advantages in pilot trials aiming to replace less predictable sulfonate partners with this compound, minimizing off-spec frequencies and stabilizing supply chains.
Study after study continues to open doors for this compound. Ongoing research focuses on its behavior in solvent-less or low-water reaction systems, especially as regulatory tides turn against volatile organic solvents. Biochemists investigate compatibility with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, searching for partners that neither denature proteins nor disrupt cell lines. Process engineers test mixtures with biodegradable solvents, aiming for “greener” reaction platforms that tick both cost and environmental boxes. The academic sphere keeps pushing on crystal engineering, where this compound sometimes unlocks access to co-crystals with pharmaceutical actives. Years working alongside interdisciplinary researchers reveal high demand for tailored coupling ions, and this material fits new requirements in reproducibility and robustness. Patents tick up each year, underscoring ongoing confidence in new uses.
Toxicology teams run painstaking studies into how sulfonate and ammonium chemistry interact with human health and the natural environment. Limited acute oral and skin exposure data show low toxicity, but long-term biological impact studies keep expanding. Environmental scientists probe breakdown rates in wastewater, watching for persistent pollutants or micro-contaminant creation. So far, results from aquatic toxicity assays and in vitro cellular screening suggest low concern at typical lab usage levels, though larger-volume disposal warrants monitoring. Having worked adjacent to compliance audits, I’ve seen how even low-hazard compounds draw regulatory scrutiny as production scales up. As safety profiles evolve, users stay alert for updates, trusting that early openness—accurate labeling, full SDS transparency—is a shield against foreseeable risk.
Several pathways open up as technology moves forward. Adoption into greener process chemistry aligns with industry aim to cut environmental impact without losing reliability. As pharmaceutical and specialty materials manufacturers stretch to meet lowered VOC thresholds, demand for ionic species that deliver on both performance and sustainability increases. Further tweaks in structure—swapping aromatic components or tinkering with hydrophilic-lipophilic balance—promise new applications in electronic materials, surfactant science, and even as mediators in bio-based manufacturing. At conferences and trade shows, enthusiasm grows around customizable salts and task-specific ion pairs. Looking at where things are headed, more research will dig into lifecycle sustainability, biodegradable analogs, and real-time safety monitoring, so this compound’s story reads more like a launchpad than a dead-end.
Folks in the chemical trade come across all sorts of tongue-twisters, and (2-Hydroxy-1,1-Dimethylethyl)Ammonium Toluene-4-Sulphonate is certainly one. I’ve had my fair share of afternoons flipping through technical datasheets, mumbling names like this one while checking if the coffee’s still hot. Even though that name looks like alphabet soup, this compound shows up in some important spots across manufacturing, research, and industry.
One role that stands out for this compound is as a phase-transfer catalyst. Anyone who’s ever poked around a chemistry lab learns quickly—lots of substances won’t just mix and react unless you coax them together. That’s where a phase-transfer catalyst comes in. It gives a nudge so that water-soluble chemicals and oil-soluble chemicals interact and do what they’re supposed to. This is a big deal for people making things like pharmaceuticals, flavors, pesticides, or specialty plastics.
Chemical reactions need to work right, or entire production lines get backed up. From what I’ve seen, companies put a high value on these catalysts because they help boost yields. That means less waste, more product, and fewer headaches over incomplete reactions or clogging reactors.
On the plastics front, (2-Hydroxy-1,1-Dimethylethyl)Ammonium Toluene-4-Sulphonate can step in as a polymerization regulator. Scientists in the rubber and resins world use it to steer how long polymer chains grow. This matters because chain length shapes a plastic’s strength and flexibility. If the process gets out of hand, you might end up with brittle batches or sticky gunk instead of sturdy material. In my own experience working at a small injection molding shop, attention to this part of the process kept jobs running smooth and customers happy.
To me, one of the underrated uses comes in surfactant science. Surfactants lower surface tension—think of how soap helps oil and water mix. The p-toluenesulfonate part of the molecule helps this compound serve as a cleaner and emulsifier. It’s still mostly behind the scenes, not as familiar as household detergent, but it makes modern cleaning and formulary work possible.
Surfactant action means easier mixing, brighter dyes, more stable paints, and slicker coatings. That cuts down on waste in factories and keeps paints from separating in the can. In other words, I’ve seen how the stuff that starts in a chemistry lab ends up making life outside work a lot more convenient.
Not all technical magic is pure upside. With chemical catalysts and surfactants, safety and runoff matter. Reliable handling procedures and labeling help protect workers. It frustrates me to see companies skip material safety training—it only takes one accident to create big problems. Proper storage, ventilation, and disposal routines keep toxicity and spill risks in check. The chemical industry as a whole has moved toward more responsible practices, in line with the EPA’s ongoing assessments.
As industries demand cleaner, more efficient processes, specialty chemicals like this one won’t fade out soon. There’s always room for innovation—greener formulations, safer handling, substitutes for hazardous reactions. Chemists and engineers who stay curious, keep learning, and adapt with new technology help push things forward.
Whether it’s pharmaceuticals, plastics, or coatings—behind all the jargon, the story is about making products work better and keeping people safe. That’s where compounds like (2-Hydroxy-1,1-Dimethylethyl)Ammonium Toluene-4-Sulphonate reveal their value.
Working with any chemical calls for more than just reading the label. Accidents often start with small acts—like skipping the gloves, or not bothering with eye protection for a “quick” task. Little mistakes send people to the ER all the time, from simple skin burns to fumes that make you lightheaded. Having spent years working in a warehouse filled with cleaning agents and industrial solvents, I’ve seen how comfort breeds carelessness. Nobody means to spill acid, but once it happens, nobody forgets the lesson, either.
Chemicals come with their own set of risks. Some give off vapors that mess with your breathing. Some corrode skin, ruin eyes, or ignite unexpectedly. Every major health agency—from OSHA to the CDC—keeps lists of workplace injuries that could have been prevented with good handling habits. Even a mild irritant can turn ugly if it splashes your face or soaks your hands day after day.
Protection doesn’t have to be complicated. Gloves shield your hands from harsh liquids. Goggles stop burning stings before they start. Lab coats or chemical-resistant aprons stop spills from soaking through clothes to your skin. My early mistakes included thinking I could “just be careful” instead of bothering with sleeves—until I had to rinse a caustic cleaner from my arm. That ten seconds was enough to lock in a habit for life.
Reliable storage means sealed containers and clear labels. Mixing chemicals without checking instructions—bleach and ammonia, let’s say—lets out toxic gas, no matter how smart you feel at the time. Allowing containers to sit open or forgetting to tighten the cap means vapors get into the air, where they can trip fire alarms, trigger asthma, or make you dizzy and unfocused.
Spills shouldn’t be left for “later.” Having cleanup supplies within reach and using them right away prevents bigger messes. I once saw a slick floor turn a routine delivery into a broken wrist for a coworker who rushed through a hallway. Since then, any spill gets sand, absorbent pads, and warning cones—without exception.
A safety meeting seems dry, but the stories you hear there remind everyone what’s at stake. Updates from the EPA and product makers aren’t just for managers. They help keep the person on the front line aware of changes in procedure, new hazards, or common signs of exposure, like headaches or a skin rash. Nobody should have to guess at first aid: clean water stations, eyewash kits, and emergency phone numbers belong within sight.
Making safety a habit beats relying on luck. Open conversations about near misses let teams work out better ways of handling dangerous materials. Introducing safety checklists stops important steps from getting skipped during busy shifts. Supervisors who set an example—wearing gear, closing bottles, checking expiration dates—show that the rules aren’t just for show.
The best workplaces treat safety not as an extra chore, but as part of doing the job right. Worry less about looking “tough” and more about keeping yourself and others healthy enough to enjoy clocking out at the end of the day.
If you’ve ever tried following a baking recipe and swapped sugar for salt by accident, you know how much ingredients change the outcome. Chemistry works the same way. The chemical structure of a substance acts like a recipe, showing which atoms link together and how they connect. Even one small swap can change the whole story. Chemists use this structure to predict reactions, spot risks, or hunt for better medicines.
Think of a chemical structure as a roadmap, but instead of city blocks and intersections, it maps out carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and other atoms. For caffeine, this “roadmap” has rings, double bonds, and branching bits. These connections decide how caffeine perks you up instead of putting you to sleep. Every medicine, vitamin, or industrial chemical springs from its structure.
Research published in Science reminds us: a single tweak in how atoms attach made the difference between Thalidomide’s safe form and the one that caused birth defects. Structure doesn’t just sit on paper — it decides what touches our lives.
Where structure tells *how* atoms connect, the molecular formula simply counts the types and numbers. For water, it’s H₂O: two hydrogen atoms, one oxygen atom. For table sugar, it’s C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁. This shorthand helps chemists spot whether compounds might act alike. Walk into a lab, and every bottle, powder, or liquid comes with a label listing its formula.
The formula can’t tell you everything, though. Glucose (the sugar in your blood) and fructose (the sugar in fruit) both show C₆H₁₂O₆, but their structures aren’t twins. That’s one reason those “energy” drinks sometimes leave you jittery—they favor a different arrangement that your body burns fast.
Chemical disasters have taught tough lessons. In 1984, a gas leak at a pesticide plant in Bhopal, India, killed thousands—partly because those handling the chemicals misunderstood the exact compound they were dealing with. Knowing both structure and formula can save lives, steer drug design, or cut pollution risks.
Fake drugs often have the same molecular formula as the real deal but slip in a few swapped bonds or extra atoms. That can mean a treatment fails or, worse, poisons the patient. Regulatory agencies worldwide now require strictly detailed chemical identifiers for every batch of medicine.
Too many science classes gloss over the details, teaching formulas as just something to memorize for the next test. That’s short-sighted. Real chemistry connects dots between structure, formula, and effect. In my own work with student groups, drawing out structures forces everyone to think about what each bond and angle might do—students spot patterns, ask sharper questions, and remember more.
We need hands-on labs that go beyond naming chemicals, where students build simple molecules with kits or software, see how changing a double bond shifts the chemical outcome, and realize why quality control teams never stop double-checking what goes in, out, and through a factory.
Clear labeling, regular re-training, and up-to-date digital tools help keep chemists and the public safer. ChemSpider, PubChem, and similar databases let anyone—from teens to researchers—call up a structure, look at 3D models, and connect properties to real-world uses. Investments in open access to this knowledge pay off every time a disaster is averted or a cure discovered.
Knowing how atoms link and what formulas stand for isn’t just for chemists in white coats. It connects to the food on your table, the air you breathe, and the medicines in your cabinet. Understanding chemical structure and molecular formula arms us with practical tools, which I’ve seen help students, researchers, and everyday folks make smarter choices—both in the lab and far beyond it.
Not many people know the ins and outs of specialty chemicals, but those who do never take shortcuts. Chemicals like (2-Hydroxy-1,1-Dimethylethyl)Ammonium Toluene-4-Sulphonate have complicated names and very tangible risks. Mishandling them even for a few hours can trigger more than just a bad day at the lab—skin burns, respiratory issues, or even long-term workplace contamination are all possibilities if proper storage gets ignored. My time in a university research facility taught me that for every chemical incident, there's usually a small act of carelessness at the root. Storage routines seem simple on paper, but real-life distractions creep in fast. One spill or a poorly sealed container creates havoc and paperwork, and just dealing with the aftermath wastes hours and frays nerves.
This compound doesn’t like heat, nor does it tolerate humidity. Most manufacturers outline temperature limits, and the best practice keeps similar chemicals in cool, dry rooms—ideally under 25°C. Humidity speeds up unwanted reactions and sometimes degrades the compound. In one small manufacturing shop I visited, an air conditioner failure on a hot, sticky summer day led to a sticky residue forming on the shelves—reminding everyone that even one careless day can threaten a whole production batch. Ventilation matters just as much. Vapors and dust build up quietly, and with enough time, respiratory hazards emerge. If you can smell it, you’re already late to the game. Fume hoods or properly ventilated storage rooms keep exposure low and workers healthy.
Some chemicals get along poorly with others. Store this one far from oxidizers, acids, or bases. Mixed storage areas often lead to accidental spills or, worse, reactions that no one anticipated. One facility I consulted for had never revised its chemical inventory, letting incompatible items sit on the same shelf for months. This meant nonstop anxiety during inspections—and a near miss when a leak appeared. Containers should be closed tightly, with clear labels that never fade. The risk isn’t just someone mixing the wrong ingredients; it’s also the chance of failing to identify a leaking or corroding bottle after years in the back row. Regular inspections keep people and spaces safer.
Hands, eyes, and lungs face the greatest danger around chemical storage. Gloves, safety goggles, and proper masks aren’t only for lab workers—they prevent hospital trips and long recovery times. I’ve seen smart, careful staff forget a glove just once, leading to chemical burns that cost much more than a few minutes’ inconvenience. Training young staff always means repeating the basics and enforcing the rules. No batch run or experiment should start until every piece of protective gear sits where it belongs.
Once safe storage becomes routine, accidents drop off quickly. People new to the industry ask why the rules seem so strict. Years of experience show that every guideline written in a safety manual comes from a real incident, sometimes painful and costly. If you work with compounds like this, treat each bottle as unpredictable until proven otherwise. Smart storage backs up your diligence—and keeps your team safer, too.
Dealers and users both feel the pressure when it comes to chemical compatibility. Years ago, I saw a small manufacturing shop lose a costly batch because someone mixed two products listed as “generally safe.” The resulting cloud of fumes forced an evacuation. Confidence in a material depends not just on what it does alone but also on what it meets. Stability with one reagent doesn’t guarantee a safe outcome with the next. Anyone who handles chemicals learns to respect this almost instinctively—after all, a little lapse goes far beyond a ruined experiment.
The industry remembers high-profile incidents. At a fertilizer plant, careless blending of ammonium nitrate with organic material set off a chain reaction no one controlled. The story repeats in labs and factories of all sizes. The difference often lies in one gap in knowledge or overlooked footnote. Compatibility isn’t a static property. Temperature, container material, and even the order of mixing can flip the switch from safe to dangerous. The science supports this: Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) list scores of incompatibles for a reason. Sodium hypochlorite and acids form toxic chlorine gas, and solvents like acetone will erode plastics that other chemicals tolerate.
Most of us rely on brands or product labels to guide these decisions. In my work, I’ve seen the assumption that commercial cleaners mix safely in the same bucket. In reality, ammonia-based cleaners do not go with bleach—poisonous gas forms in an instant. Chemists, pharmacists, and cleaners face different scales of risk, but the story remains the same: Respect the reactivity chart. There’s a reason so many product sheets arrive packed with warnings. Those who read closely stand a better chance of preventing disaster.
Customers deserve more than marketing promises. Evidence sits in real data, test results, and peer-reviewed studies. If a manufacturer claims broad compatibility, check their research. Have they documented stability with the specific reagents in question? Did their testing include different temperatures or storage times? Sites like PubChem and published journals reveal unexpected hazards. In my experience, open lab notes prove more useful than a glossy brochure. Many companies invite questions—sometimes a call or email turns up unpublished testing or caveats not found on the label.
Stronger training sits at the front of progress. Years ago, companies simply handed out safety goggles and hoped for the best. Now, regular workshops and digital tracking raise awareness of incompatibility risks. Suppliers can post clear, digital compatibility charts instead of burying details in fine print. QR codes leading to interaction tables or up-to-date bulletins make a difference—instant access shrinks room for error. Product developers do their part by listing tested pairings and exclusions in plain language.
Responsibility goes both ways. Buyers should demand access to transparency when investing in new materials. Suppliers should build support beyond sales—technicians often have a sharper eye on what actually happens in the field. Sharing real stories about close calls and safe solutions adds valuable experience to the rulebook.
Compatibility doesn’t just belong to chemists. Every industry using chemicals, from agriculture to food service, faces these questions. The push for safety, value, and reliable outcomes links us all—and clear, tested answers help everyone sleep a little easier.
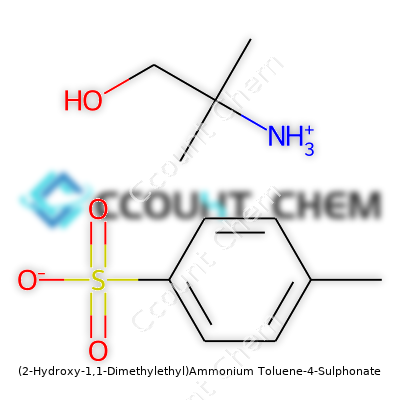
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropan-1-aminium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate |
| Other names |
2-tert-Butylaminoethanol 4-methylbenzenesulfonate 2-(tert-Butylamino)ethanol 4-methylbenzenesulfonic acid t-Butylaminoethanol p-toluenesulfonate 2-Hydroxy-1,1-dimethylethyl)ammonium p-toluenesulfonate |
| Pronunciation | /tuː ˈhɒk.si waɪ wan waɪ daɪˈmɛθ.əl ˈɛθ.əl æˈmoʊ.ni.əm təˈluː.iːn fɔːr ˈsʌl.fə.neɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 145671-34-7 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1718736 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:131189 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1201201 |
| ChemSpider | 16736864 |
| DrugBank | DB13751 |
| ECHA InfoCard | ECHA InfoCard: 100_080_204 |
| EC Number | EC 248-809-7 |
| Gmelin Reference | 4225683 |
| KEGG | C21189 |
| MeSH | D017379 |
| PubChem CID | 139645857 |
| RTECS number | GR1575000 |
| UNII | Z79T9I6R6X |
| UN number | UN3261 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C11H19NO4S |
| Molar mass | 259.36 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.24 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | soluble |
| log P | -1.2 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.21 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 6.77 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -69.49·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.530 |
| Viscosity | 450 cP (25 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 7.03 Debye |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -534.3 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if swallowed. Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS07, GHS05 |
| Pictograms | GHS07 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-1-0 |
| Flash point | > 174.5 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 Oral Rat: 1750 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral rat LD50 > 2000 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | Not assigned |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not Established |
| REL (Recommended) | 10 mg/m³ |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Not established |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Toluene-4-sulfonic acid Trimethylamine Tert-butanol Ammonium toluene-4-sulfonate p-Toluenesulfonamide Tert-butylammonium chloride Tert-butylammonium bromide |