Interest in (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid traces back to the expanding frontiers of alkaloid chemistry in the late 1800s. Organic chemists scouted for new ways to resolve chiral alkaloids and found camphorsulfonic acid to be a potent agent. Its strong acidity and configurational stability quickly marked it as a reliable resolving agent well into the 20th century, especially as the pharmaceutical sector exploded. Advancement in stereoselective catalysis led research circles to revisit molecules like camphorsulfonic acid, relying on its robustness and predictable behavior. Over decades, it has become a staple in chemical synthesis labs and manufacturing floors alike, with universities using it as a teaching example for asymmetric synthesis. The trust in its effectiveness can be traced to the robust, methodical experimentation of the early pioneers in stereochemistry and practical organic chemistry.
Today’s chemists prize (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid for its ability to carry out precise chemical transformations. Available in crystalline, odorless form, the compound shows outstanding purity, often exceeding 98%. Commercial shipments often arrive packed in moisture-resistant drums or amber glass bottles, with every batch identified by precise batch numbers and purity certificates. Supply chains maintain tight control over storage and traceability to meet the constant quality demands from pharmaceutical manufacturers and academic researchers. Availability of enantiomerically pure forms has vastly expanded its usage beyond historical limits, building direct bridges between small-scale research and industrial-scale chemistry.
Physically, (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid shows up as white to off-white crystalline powder, with a molecular weight near 232.3 grams per mole. It resists decomposition up to around 180°C, allowing for safe transport and storage. The substance dissolves easily in water and many polar organic solvents, including methanol and acetone. Its specific rotation stands clearly negative, confirming its stereochemical identity. Chemists note its sharp melting point, a detail that proves useful for purity assessment and reaction planning. Its strong sulfonic acid group lends the molecule substantial acid strength, and its chiral structure remains rigid under typical reaction conditions.
Labeling adheres to global standards for chemical identification. Labels indicate IUPAC names, hazard alerts, batch numbers, expiry dates, and the supplier’s contact details. The regulatory documentation often includes detailed safety data sheets, which walk through first aid, shelf life, recommended handling temperatures, packaging types, and transportation codes. These technical specifications support traceability and transparency, key principles in chemical manufacturing and laboratory supply. Authentic product ships with analytical datasheets that list HPLC or GC results, moisture content, and residual solvent analysis—offering peace of mind for end users who rely on Traceability and Product Integrity in regulated environments such as pharmaceutical research.
Synthesis usually begins with native camphor, chosen for its availability and stereochemistry. Chlorosulfonic acid acts as the sulfonation agent, reacting with camphor under mild exothermic conditions, and the crude product undergoes re-crystallization to achieve high purity. Isolation of the enantiomer is accomplished using chiral resolving agents or by attentive crystallization practices. Over time, process chemists have scaled the method from bench-top flask reactions to robust batches with attention to waste management and operator safety. Purification steps incorporate active charcoal, filtration, repeated re-crystallizations, and drying to strict specifications, securing the tight tolerances demanded in pharmaceutical ingredient manufacturing.
(1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid enables remarkable versatility in organic synthesis. It features heavily as a catalyst in acetalization, esterification, and glycosylation reactions, making it a backbone material in the fabrication of rare sugars and specialty pharmaceuticals. The acid group tolerates further conversion to sulfonate esters or salts, useful for phase-transfer catalysis. It readily forms salts with basic drugs, simplifying purification through selective precipitation. Some synthetic chemists perform modifications on the camphor skeleton, producing derivatives for stereochemical studies and pharmacological evaluation. Its well-defined chiral center supports resolution of racemic mixtures, especially valuable in both academic research and preliminary stages of drug development.
Different industries and catalogs know (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid by alternate names, including Camphor-10-sulfonic acid, CSA, and S-(+)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid. Catalogs often list it as CAMPHORSULFONIC ACID-(1R,)-(-), and many research circles shorthand the name to CSA in lab documentation. Trademarked names or regional supplier codes add further variety, requiring users to cross-reference CAS numbers (5872-08-2) to ensure compatibility when ordering across different markets. Pharmaceutical supply chains often restrict product names to validated references to comply with the patchwork of international regulatory agencies.
Handling pure camphorsulfonic acid demands basic protective gear—lab coats, nitrile gloves, safety eyewear—because skin and respiratory contact can cause irritation. Storage occurs in cool, dry rooms, with containers kept tightly sealed to prevent moister uptake. Ventilated fume hoods or gloveboxes stop inhalation risks during weighing and transfer. Safety Data Sheets document first aid procedures, spill recovery, and chemical disposal alignment with local regulations. Regulatory agencies include the compound on lists requiring reporting and proper registration, and many industrial sites train staff with mock drills focused on acids like this. Disposal follows waste neutralization procedures, often ending with transfer to authorized hazardous waste handlers.
Chemists rely on (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid for resolving chiral bases in both small-batch R&D and routine production. Its chief customers include pharmaceutical drug manufacturers, who need enantiomerically pure salts for active pharmaceutical ingredients. It also finds use in total synthesis of complex molecules, where stereochemistry unlocks or blocks biological activity. Paint and coating industries occasionally use it as a solid acid catalyst, and some advanced material laboratories call for it in chiral templating and polymer modification studies. Even outside bench laboratories, formulation scientists in biotechnology consider it a staple reagent, where purity and predictable reactivity trump all else.
Current research keeps pushing the limits of what this molecule can contribute. Efforts target more efficient synthetic routes and greener processes to satisfy sustainability demands from regulators and consumers. Ongoing studies probe its ability to act as a chiral catalyst in asymmetric reactions, which could reshape how future drugs are built. Analytical chemists develop rapid tests for residual amounts in pharmaceutical products, keeping patient safety top of mind. Multinational research teams compare its efficacy in resolving different classes of alkaloids and apply advanced spectroscopic techniques to reveal nuances in its solid-state behavior. A growing focus on automation and process analytical technology seeks ways to integrate camphorsulfonic acid seamlessly into continuous flow synthesis.
Toxicologists look hard at all facets of exposure. Animal studies have traced the limits of oral and dermal toxicity, finding moderate short-term effects and no alarming long-term bioaccumulation when handled correctly. Regulatory dossiers review ecological risks, monitoring possible entry into water streams or soil and ensuring that workers face minimal risk through regulated exposure regimes. No stories of major incidents have emerged in the literature, but safety always stays ahead of complacency. Risk analyses recommend further chronic toxicity studies, especially as production volumes and application areas expand into new fields. Modern industrial hygiene practices address most concerns, with incidents rare in professionally managed environments.
The future for (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid remains bright—especially as pharma and materials science both demand greater optical purity and greener processes. As chemical engineering pivots to more sustainable and scalable solutions, this molecule’s established chemistry and reliable availability offer practical stepping stones. Research collaborations pour resources into new derivatives and applications, eyeing better catalysts and sophisticated building blocks for modern synthesis. University curricula continue treating it as a workhorse example for stereochemical control, promoting the next generation’s deep understanding of chirality and its practical industrial value. Its journey from niche resolving agent to foundational, multi-purpose acid reagent captures much of how chemical science adapts old wisdom to solve new-age challenges.
People in labs place a lot of trust in the purity label on a reagent bottle. Even a small deviation can mess up an experiment, slow down a synthesis, or lead to wasted money. (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid, often used to prepare chiral catalysts or resolve racemates, gets attention for its enantioselectivity and, crucially, its purity level. Checking for a number like 98% or 99% on the label is only the start. Suppliers usually base those numbers on high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or melting point analysis, but a single test can't tell the whole story.
Chemical purity isn’t just about what’s absent — it’s about confidence in what’s present. Many batches coming out of the manufacturing process start at high purity, but handling, packaging, or even exposure to air eats away at those numbers. Sulfonic acids can easily pick up traces of water, dust, or residual solvents if left open. In the right climate, moisture in the air can start to dissolve some acids at the surface, leading to misleading weights or unexpected results.
If you’ve spent time at the bench, you’ve probably fought with some persistent crystallization problems. Sometimes impurities lurk at a fraction of a percent yet cause cloudiness or throw off optical rotations. Not every impurity shows up in standard tests. A batch may meet 99% purity by HPLC but still have enough chiral or non-chiral byproducts to complicate a reaction. Careful researchers push past the certificate of analysis and look for supplier transparency about the remaining 1%. Are those other compounds volatile? Do they include unreacted camphor, leftover sulfuric acid, or unusual sulfonate byproducts?
Academic researchers working on new chiral ligands know a trace impurity might mean hours lost troubleshooting unexpected byproducts. In industrial runs, those small contaminants can make large differences in product isolation steps, affect yields, or show up in regulatory filings. Several pharmaceutical syntheses rely on camphorsulfonic acid for optical resolution, so batch-to-batch purity differences can impact downstream safety and efficacy of drugs. The quality range matters most in sensitive chemistry — such as creating enantiopure compounds where the wrong impurity can flip a stereocenter or destroy selectivity.
Labs and procurement teams help themselves by demanding analysis beyond basic purity specs. A good policy includes routine NMR checks alongside HPLC and mass spectrometry to catch non-obvious contaminants. For crucial jobs, labs often buy from multiple suppliers, then match the reagent’s performance before picking a “go-to” source. Open communication with suppliers helps, especially when pushing for batch-specific data, residual solvent levels, or specific impurity profiles.
Proper storage also keeps purity stable. Dry, sealed bottles, kept away from light and temperature swings, stay within spec longer. For high-stakes syntheses, even weighing out samples inside a glovebox can pay off if the compound absorbs water easily. Even routine habits, like wiping spatulas and keeping lids closed, protect sensitive chemicals.
Researchers looking for consistent results can’t only trust the number on the label. Purity needs constant verification—through technical questions, secondary tests, and controlled storage. Labs that put in this effort avoid costly reruns and unexpected byproducts, and they get a lot closer to reliable chemistry every time they draw from that camphorsulfonic acid bottle.
Working a few years in pharmaceutical labs, you learn to spot the unsung heroes early. Take (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid—a mouthful of a name, yet central in more discoveries than most people realize. It is popular among chemists not because it is flashy, but because it gets things done with precision where other acids stumble.
Many blockbuster drugs rely on molecules that are handedness-specific. This acid earns its keep as a reliable chiral resolving agent. Imagine a molecule that comes in two mirror images—like left and right hands. For medicines, picking the right one makes all the difference. Too often, a batch will include both forms. That’s not just a technical hiccup. It can mean the drug works as intended or causes side effects. (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid helps split these pairs, anchoring the right version so manufacturers can fish out exactly what doctors need to prescribe. I’ve seen teams spend days shaving time off a synthesis; using this acid brought down error rates and sped up the workflow without exotic equipment.
Researchers aiming to craft new molecules run into delicate reaction conditions. Some processes depend on having both strong acid strength and selectivity—think big-name catalysts like trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, but less aggressive and easier to handle. That sweet spot is where camphorsulfonic acid comes in. It acts as a catalyst for key steps like acetal formation, and for making ethers or esters. Its ability to direct reactions without tearing up sensitive starting materials means more successful experiments, less wasted time, and budgets that stretch further. Many university labs reach for it while training chemists, since the results build trust in foundational lab skills.
The growth of green chemistry highlights enantioselectivity more than ever. Industry is under pressure to get clean products, avoid sloppy byproducts, and reduce waste. (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid fits that mindset. In the synthesis of optically active compounds for sophisticated materials—think of liquid crystals for new types of screens or high-performance polymers for aerospace parts—this acid steps up. These roles demand a catalyst that guides every step with control. My own experience with alternative acids cannot match camphorsulfonic’s repeatable results, especially in tight timelines.
Where solvents get fussy, water-sensitive, or hard to purify, camphorsulfonic acid simplifies cleanup. It dissolves easily, so residue rarely gums up equipment. Startups in pharma and materials research pick it for both small-scale trials and scale-up production. From the regulator’s viewpoint, process consistency and clean product batches mean smoother approval filings. In an era where small mistakes can stall entire pipelines, reliable reagents like (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid keep the gears turning.
As the chemical industry keeps pushing for safer, greener, and more effective ways to make medicines and materials, the value of robust acids that offer both selectivity and power will only rise. Backed by decades of published research, (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid ranks as an essential reagent—quietly solving problems today and setting the stage for next-generation breakthroughs in chemistry.
Anyone who has worked in a chemistry lab knows strong acids never get handled casually. (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid, known for its distinctive aroma and solid granules, offers plenty of utility in organic synthesis, but it demands careful storage. Keeping a compound stable and safe involves more than following a checklist. Practical habits, rooted in real lab work, are what set apart a safe space from a risky one.
Every chemist has fished a damp clump out of a loosely capped bottle. This acid loves to absorb moisture—left out, it clumps and dissolves on its own. Humidity not only eats away at its shelf life but turns weighing into a guessing game. Moisture can even cause low-level decomposition, messing with sensitive synthesis steps.
Choose dry, air-tight containers. Screw caps beat stoppers. Parafilm helps, but nothing replaces a well-chosen plastic or glass bottle with solid threading. Keeping bottles low in the fume hood may seem convenient, but the best place will always be a cool, bone-dry storage cabinet. Even in busy university labs, silica pouches and a labeled, low-traffic drawer outperform leaving it out on an open shelf.
This acid handles room temperature well, but direct sun or a heat source warps the story. Heat boosts reactivity and piles on trouble if other bottles stand too close or temperature swings hit hard. Risk spikes in the summer, especially in labs without reliable climate control.
Most chemical storerooms offer stable, dim conditions—ideal for keeping things calm. I’ve seen what happens when a bottle sits near a sunny window: yellowing, plastic warping, and a cleaning headache if a leak sets in. Drawers or cabinets away from radiators or windows make life easier.
Strong acids deserve clear labels. Training sessions sometimes skip over the simple step of bold, waterproof labeling. People work faster, bottles get juggled, and anyone new to the bench might grab the wrong acid if labeling goes sloppy. Adding hazard symbols, date received, and the chemical’s full IUPAC name means fewer mix-ups.
Acids react with bases and certain metals. It surprises no one when a shelf spill turns into fizzing drama, but the best way around this involves good old-fashioned segregation. Keep acids apart from anything alkaline. Never tuck a sulfonic acid bottle in the same box as sodium hydroxide pellets. Separate shelves, labeled bins, and a culture of double-checking make a real difference.
No matter how careful you are, spills happen. Quick action keeps little accidents from turning big. I always keep spill kits nearby—baking soda, gloves, and absorbent pads work for most labs. Pouring leftovers down the sink never sits well with environmental rules or safety officers; always follow chemical waste guidelines laid out by your institution. Good storage routines pair with responsible, traceable disposal.
People handle acids safely if they know exactly why every step matters. Training, whether it comes from a senior, a poster, or a quick team debrief, shapes habits that last. Regular checks of storage areas catch leaks, expired bottles, or encroaching humidity before they turn into bigger problems. That, in my experience, keeps both chemistry and people out of unnecessary trouble.
Every chemist can tell you about the headaches that come from ambiguous chemical names. I’ve been in that spot before, searching for a reagent and finding that it goes by five different names and half a dozen structural notations. For (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid, confusion grows because the name twists and turns with stereochemistry and sulfonation details that only specialists remember offhand. The CAS Registry Number cuts through all this fog.
The CAS number, 5872-08-2, draws a clean, sharp line. It’s more than just digits; it’s a worldwide reference, locking in precisely one compound in a sea of similar names and formulas. In the lab, that's a safety net. You don’t worry about grabbing the “wrong camphorsulfonic acid” – a mistake that wastes time and money or even jeopardizes an experiment. Pull up a material safety data sheet, order reagents, or check regulatory approvals: that number means you’re all talking about the same substance, no matter the language or supplier.
I’ve worked with young researchers struggling to track down the right standard for asymmetric synthesis. Camphorsulfonic acid shapes reactions and chiral environments, but there are other camphor derivatives with close names. One missed letter in a request form leads the storeroom to ship the wrong bottle. If you tap in CAS 5872-08-2, the margin for error evaporates. This goes way beyond convenience. Projects rely on reproducibility, and matching CAS numbers builds a foundation for trust across labs and universities. Suppliers, safety boards, and customs officers — all lock eyes on that registry number, preventing expensive delays or even legal hitches.
The same principle runs straight through to big industry. Pharmaceutical teams don’t gamble on ambiguity when tracing batch origins or reporting to regulators. Think of the paperwork for a new drug application, stacked with references and purity checks. Consistency hinges on every detail, and the CAS number establishes a rock-solid link to the right molecular identity, supporting good documentation practices and food and drug authority audits.
Chemical safety reaches into public health and the environment. The wrong chemical waste, misclassified in a shipment, spells trouble—accidents, fines, or contamination. Using CAS 5872-08-2, companies accurately report toxicology data and handle disposal guidelines tailored to (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid and not a close cousin. This level of precision lines up with responsible manufacturing and green chemistry initiatives, as tracking every chemical’s life cycle starts with clear identification.
It’s worth insisting on CAS numbers for every chemical purchase and data set. I’ve seen teams adopt digital systems that auto-check the CAS number before signing off on orders or shipments. Training new lab members to spot errors here makes a huge difference, leading to smoother compliance and safer research. Some organizations even bake CAS checking right into their safety protocols and environmental monitoring, boosting their reputation for integrity and transparency.
The CAS number for (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid, 5872-08-2, does a quiet but powerful job. It removes guesswork, locks in reproducibility, and points everyone in the right direction, whether you’re running a student lab or spearheading a vital industrial process.
(1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid, sometimes just called camphorsulfonic acid, looks pretty tame at first glance. It’s a solid, white powder that doesn’t send people running for the safety shower. Seeing it in the bottle, you wouldn’t think twice if you didn’t know chemistry. The reality is, it does bring some risks, and you need to treat it with the respect other strong acids get.
This acid can eat through skin and eyes if you give it half a chance. I remember the first time a small pinch hit my glove—felt like nothing at first, but within seconds it started burning. Strong enough that even the vapor off a concentrated solution makes you cough. Safety data sheets rate it as hazardous, not just a mild irritant. Left out, it’ll chew through whatever it sits on, especially in humid air, because it grabs at water and keeps reacting.
Anyone using camphorsulfonic acid in the lab or workshop really needs solid gloves, chemical goggles, and a good coat. Getting lazy or skipping protection just because it doesn’t look scary leads to burns or worse. The acid’s dust floats up easily and gets on skin or in lungs. I’ve seen folks ignore the dust mask, only to end up coughing until their chest hurt. Even minor exposure leaves a mark, especially around cuts or sensitive spots like the face and neck.
Contact with water or bases sends it fizzing and spitting, which means it shouldn’t mix with anything you’re not 100% sure about. Fuming and splattering cause more injuries than you expect, especially if you’ve gotten too casual in your routine. Some labs run fume hoods just for working with this stuff, not as decoration but because one mistake with acid dust or vapor leaves scars, not just on counters but on lungs and eyes.
People throw around the word “hazard” too much, but for camphorsulfonic acid, it fits. Sealed containers, clear labeling, and logos for corrosive materials aren’t just bureaucracy. Moisture ruins it and creates secondary hazards like slippery floors or new acids forming in storerooms. Leaving a scoop or spatula in the jar builds up crusty, dangerous residue. Dumping leftovers in the trash or sink invites hotline calls and visits from inspectors. A spill kit for acids and a shady spot away from sunlight beat improvisation every time.
You don’t need a million-dollar lab to suffer a nasty burn or cause an environmental problem. Recipes online for making custom catalysts, or DIY organic synthesis, often gloss over how ugly a spill or bad reaction can get. It’s on every user—student, hobbyist, or researcher—to read the safety sheets, use personal protection, and store the acid safely. Emergency rinses and neutralizers sound like overkill until they save skin and eyes in an accident.
Camphorsulfonic acid doesn’t “look” bad, but looks deceive. Treating it like any other strong acid is the only way to avoid turning a simple chemical task into a medical emergency. Facts, experience, and a dose of respect beat wishful thinking and shortcuts every day.
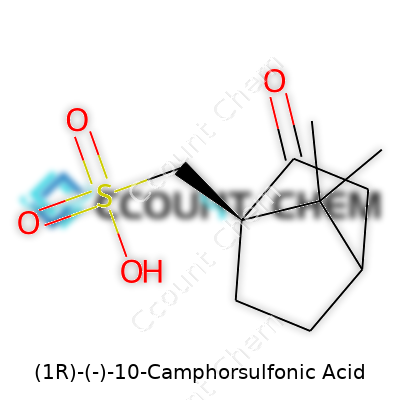
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | (1R)-1,7,7-Trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-one-10-sulfonic acid |
| Other names |
(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid CSA Camphor-10-sulfonic acid (1R)-(+)-10-Camphorsulphonic acid (R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid |
| Pronunciation | /ˈwʌn ɑːr ˈmɪnəs tɛn kæmˈfɔːrˌsʌlˈfɒnɪk ˈæsɪd/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 5872-08-2 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1720529 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:64302 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL107105 |
| ChemSpider | 53613 |
| DrugBank | DB04115 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 01a686af-96e1-431a-ab8f-7bfa4235c8bc |
| EC Number | 227-022-6 |
| Gmelin Reference | 63900 |
| KEGG | C06251 |
| MeSH | D002189 |
| PubChem CID | 18749 |
| RTECS number | RH0475000 |
| UNII | 22T1X928EB |
| UN number | UN3261 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H16O4S |
| Molar mass | 232.31 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.252 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | soluble |
| log P | -1.3 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0000711 mmHg at 25°C |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.2 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 1.2 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | –7.42 × 10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.558 |
| Dipole moment | 3.70 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 187 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive, causes severe skin burns and eye damage, harmful if swallowed or inhaled. |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS05, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS05, GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302, H318 |
| Precautionary statements | P280-P261-P264-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P301+P330+P331-P303+P361+P353-P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 3-1-2-酸 |
| Flash point | 174 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 400 °C |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose) of (1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid: "LD50 oral, rat: 2000 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | GR1575000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 10g |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | IDLH: Not established |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Camphorsulfonic acid Camphor Camphorsulfonamide p-Toluenesulfonic acid Sulfanilic acid |