1-Propanesulfonic acid didn’t emerge overnight, and its road from obscure laboratory synthesis to multi-industry relevance reminds me of watching once-forgotten ingredients make their way to restaurant menus—there’s curiosity, adaptation, and sometimes, skepticism. Chemists in the early twentieth century pushed forward on sulfonation methods for hydrocarbons, often for dyestuff intermediates. The growing interest in surfactants and specialty chemicals through the mid-century opened doors for handling sulfonic acids, including this straightforward, three-carbon chain member. By the 1960s, as synthetic methods and purification refineries improved, scientists began using 1-propanesulfonic acid more frequently for both analytical research and specific manufacturing applications, not just as a chemical curiosity. It’s now common to find it indexed in chemical catalogs, making it accessible to researchers and process engineers who want something a bit more hydrophilic than aliphatic acids yet less harsh than aromatic sulfonates.
Meeting 1-propanesulfonic acid for the first time, one might focus on its simple structure: an unbranched propane chain capped with a sulfonic group. Lab manuals often list it as a colorless to slightly yellow, viscous liquid. Its strong acidity and high solubility in water pushes it into the spotlight for those seeking robust proton donors or mild sulfonation agents. Supply chains today catalog it under various product codes and purity standards, with suppliers catering to research, pilot-scale syntheses, and bulk manufacturing. This isn’t the sort of commodity you find rusting away on the shelf; it’s shipped in tightly sealed containers due to its strong hygroscopic nature and the need to prevent contamination. Chemists handling it look for batch-specific technical sheets that lay out active content, water percentage, and impurity levels.
1-Propanesulfonic acid, C3H8O3S, brings a molecular weight around 124.16 g/mol. The boiling point usually comes close to 242°C, and it stays stable below this, though extended heating can prompt decomposition. Its melting point runs low, often cited under 0°C, making it a liquid at most ambient lab environments. The acid trumps many other alkyl sulfonic acids in water solubility, which makes it easy to mix into aqueous systems or recover after use. Chemically, the sulfonic group gives it a high degree of dissociation, much like sulfuric acid but far less oxidizing, so it’s powerful but less damaging than concentrated mineral acids. Labels in my experience always warn of strong acidity and the risk to skin and eyes, along with the UN number for hazardous transport and standard pictograms for corrosivity and environmental hazard.
Preparation often starts with 1-propanol reacting with sulfur trioxide or chlorosulfonic acid under controlled temperatures, producing the sulfonic acid in high yield when moisture and side reactions are tightly managed. Industrial setups tweak reaction times, catalysts, and separations to bump up throughput and lower unwanted byproducts. Purification relies on vacuum distillation, crystallization from water, or extraction with polar solvents. High-grade material surfaces after careful evaporation and neutralization steps, with analytical controls hunting down any chlorinated, oxidized, or over-sulfonated trace impurities. Working through bench synthesis, I always noticed how important precise temperature control is—an overheated reactor leads to complex tars that make purification a nightmare.
Versatility defines its chemical possibilities. The sulfonic group activates the entire molecule towards condensation reactions, esterifications, and neutralizations. You’ll see sodium or potassium salts formed by simple base titration, which crystallize out and open up use in solid catalyst beds or ion-exchange systems. Researchers tinker with alkylation at the propyl chain, which brings out derivatives suited for specialty detergents or pharmaceutical intermediates. It also participates in protection and deprotection chemistry as a blocking group in peptide assembly, where acid strength and solubility become critical. Anyone who’s spent hours in organic synthesis appreciates how such a strong, stable functional group can streamline synthetic routes when combined with catalysis or used in solid form.
1-Propanesulfonic acid hides under a few guises across catalogues and technical bulletins. Sometimes it’s listed as n-propanesulfonic acid, propane-1-sulfonic acid, or 3-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid (though this last one isn’t quite the same). Trade names can differ by supplier, especially when sold as sodium or potassium salts—common in analytical chemistry as surfactant standards or buffer additives. These synonyms complicate both purchasing and literature searches; in my own research, more than once I ordered the wrong compound thanks to a mislabeled product page, highlighting the need for clarity and reliable labeling.
Any acid with strength to rival sulfuric demands respect. Spills burn and corrode—plastic gloves, eye shields, and fume hoods become the norm. Material safety data sheets spell out the acute risks: skin corrosion, eye damage, respiratory impacts from vapors. Laboratories keep neutralizing agents (like sodium bicarbonate) on hand during use. In a production setting, containment and proper ventilation matter. I’ve seen operators double up on gloves and keep emergency eyewash stations within arm’s reach. Environmental controls and wastewater protocols stop the acid from entering drainage unchecked, as its low toxicity for aquatic life is outweighed by its sheer acidity if uncontrolled. Training focuses on clear procedures and hazard communication, which lessens the chances of a careless splash turning into a serious incident.
Synthetic chemists, polymer scientists, and electroplating technicians all reach for this acid when they want strong, water-compatible proton donors that won’t bring in halide contamination. Certain catalyst prep routines use its sodium or potassium salts for selective ion-exchange, which adjust the final product profile in resins or gels. This acid also pops up in pharmaceuticals, as a mineral acid surrogate with high solubility, and in battery electrolytes. In analytical circles, it’s found as a buffer component for capillary electrophoresis, where mobility and pH stability matter. Some cleaning and degreasing products bank on its surfactant roots, especially in metal finishing. I’ve used its derivatives in synthesis where the aim is strong acidity but with less oxidizing punch than mineral acids—a sweet spot for sensitive organic molecules.
Research papers continue to surface on new uses for propanesulfonic acids, often inspired by their robust acidity and solubility. Academics and applied scientists look to functionalize the molecule for greener catalytic systems, including room-temperature chemical transformations that cut down harsh reaction conditions. Some focus on novel polymer doping using the acid or its salts, tuning conductivity and durability in electronic materials. Newer fields like ionic liquids and organocatalysis have explored its structural relatives, showing that even small changes on the alkyl chain tweak reactivity or extraction profiles. Many researchers report on improved yields or more selective product formation by using propanesulfonic acid salts as counter-ions or phase-transfer reagents. In my reading, references from the last five years specifically mention sustainable synthesis, showing a tilt in focus toward environmental compatibility.
Toxicology data paint a picture of an irritant rather than a poison—it causes burns on contact and severe eye irritation, but doesn’t accumulate in tissues or present chronic risks in trace contamination. Acute tests place its LD50 well above that of common pesticides or industrial solvents, though at concentrated exposures the acid does enough tissue damage to warrant emergency treatment. Lab rats show reversible symptoms upon low-level dosing, indicating rapid metabolism and elimination. As with many strong acids, the bigger health worry comes from accidental exposure rather than systemic toxicity. Importantly, regulatory bodies ask for strict labeling and tightly managed workplace exposures, based on documented incidents in both research labs and pilot plants where poor handling led to burns or inhalation injuries. My own safety training emphasized acid-resistant coats and ready access to eyewash, drawing on safety case studies involving alkylsulfonic acids.
Sustainable chemistry drives demand for acids that offer low volatility, high aqueous solubility, and manageable toxicity profiles—qualities 1-propanesulfonic acid carries in spades. Companies seeking to reduce hazardous waste and minimize halogen content in both upstream and downstream processes keep scouting alternatives to traditional strong acids. This acid finds a role in bio-based polymers and green catalyst design, taking over from legacy mineral acids in some procedures. Specialty battery and supercapacitor technology may push its use further if ongoing electrolyte research proves fruitful. As industrial companies and academic labs connect over open innovation initiatives, tweaks to the propyl chain or hybridization with renewable feedstocks could spawn a new family of sulfonic acids tailored for emerging market needs. I see an opening for further toxicological research, specific to long-term workplace exposure and environmental fate, to help shape new application domains and keep up with regulatory evolution. The intersection of performance, safety, and sustainability will shape its next act and keep its story unfolding in the years to come.
Some chemicals work quietly behind the scenes and often don’t make headlines, but their impact pops up almost everywhere. 1-Propanesulfonic acid fits that description. I’ve seen this compound most often in labs, but its reach goes beyond the glassware. Its most common strength comes from being a strong sulfonic acid and a decent building block for more complex chemistry.
1-Propanesulfonic acid pulls a lot of weight in chemical synthesis. In organic chemistry, it delivers sulfonate groups with surprising precision. If you've ever needed to introduce a sulfonic acid group to adjust a molecule’s properties, you’ll likely appreciate what this acid can offer. Because it's less bulky than longer-chain options, it works well for applications where minimal interference is essential.
Chemists often reach for materials that allow for easy functionalization—small changes that lead to big shifts in behavior. 1-Propanesulfonic acid brings a compact sulfonate group, letting researchers tweak molecules for things like drug discovery, dye manufacturing, or specialty surfactants. In some areas, like creating catalysts or ion-exchange materials, 1-Propanesulfonic acid stands out thanks to its solubility and reactive sulfonic group.
Industries like pharmaceuticals, oil refining, and manufacturing put 1-Propanesulfonic acid to work without much fanfare. For example, sulfonic acids often help build surfactants—key ingredients for detergents or emulsifiers. The acid’s structure makes it handy for creating water-soluble salts that stabilize products or clean up the toughest messes.
Chemical suppliers see its value in producing intermediates—those stepping stones that help turn basic raw materials into finished products. Because it throws in a highly polar group, it helps tune solubility, boost chemical reactivity, or support ion-exchange processes. One overlooked advantage shows up in electroplating or as ion-exchange resin feedstock, where it helps control process conditions or product properties.
You’ll also find sulfonic acids playing a role in fuel additives, and water treatment. 1-Propanesulfonic acid acts as a starting point for these specialty chemicals. Its moderate carbon chain length keeps things balanced: it doesn’t gum up reactions, yet still delivers the acidity and solubility that make these applications run smoothly.
Working with acids calls for common sense and a bit of respect. Any strong acid can burn or irritate skin and eyes, and 1-Propanesulfonic acid is no different. Handlers wear gloves and eyewear, and treat spills carefully. Shipping and storing this kind of chemical means following guidelines to keep risks in check.
Environmental groups keep a close eye on sulfonic acids. They push for waste streams that avoid waterway contamination, and responsible companies focus on containment and treatment. Following local and international regulations protects both workers and the wider community.
The chemical industry keeps moving towards safer, more efficient techniques. 1-Propanesulfonic acid pops up in more eco-friendly processes, where minimizing waste ranks as a priority. A push for biodegradable surfactants or safer dye intermediates means researchers pay more attention to acids like this. It serves as a stepping stone—compact, versatile, and up for the next challenge as green chemistry becomes mainstream.
In the end, 1-Propanesulfonic acid quietly anchors plenty of everyday innovations. Its value comes from versatility and reliability, whether you find it in a research lab, a product assembly line, or even in the search for greener solutions.
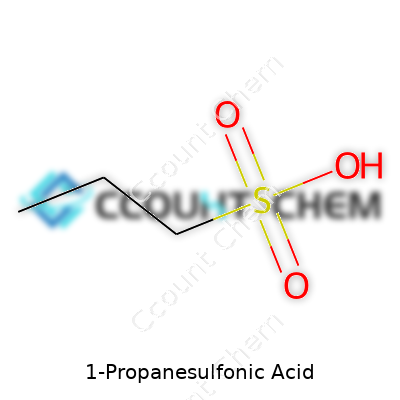
1-Propanesulfonic acid isn’t a household name, but its structure shapes how it fits into so many industries. Chemistry students and professionals often need to look closely at a substance's molecular formula to predict reactions or understand safety requirements. To spell it out, 1-Propanesulfonic acid has the formula C3H8O3S. That means three carbon atoms, eight hydrogens, three oxygens, and one sulfur atom.
For anyone who’s studied organic compounds, the structure makes sense—start with propane, three carbons in a row, then swap a hydrogen from the first carbon for a sulfonic acid group. A true test of understanding comes from seeing how slight tweaks give rise to very different molecules. For instance, shifting the sulfonic acid to another carbon on the chain produces a different compound, changing physical and chemical properties all over again.
In the chemistry lab, you don’t just mix chemicals for fun—a clear grasp of molecular structure and formula keeps reactions predictable and reproducible. Having worked on projects involving surfactants and organic synthesis, I’ve seen how 1-Propanesulfonic acid acts as a useful building block for chemical synthesis or for crafting specialty detergents and catalysts. Such molecules can steer the course of a process, influence yield, and affect environmental outcomes.
Documenting an outright formula isn’t just about quizzes or memorization drills. It’s about tracing how atoms join and interact. Even minor mistakes in formula notation can spell disaster: incorrect labels lead to wasted resources, ruined experiments, or even health risks. In regulated industries, those tiny details matter not only for results but also for compliance.
Chemically, 1-Propanesulfonic acid carries a sulfonic acid group at the end of a three-carbon chain. That group is known for being a strong acid, more acidic than most organic acids thanks to the highly electronegative sulfonate ion. Substances like this one see their main opportunity where strong acids and water solubility are required—such as in pharmaceutical research, organic synthesis, and select cleaning agents.
Data shows sulfonic acids are less volatile, so spills and leaks pose fewer inhalation risks compared to mineral acids. Still, safe handling calls for gloves and goggles, and that’s something you can’t skip just because the formula looks benign. The debate around industrial acid use highlights why formulas aren’t just academic—they’re tied to safe handling and best practices every day.
Formulas give us more than a snapshot. They give professionals and students a reliable way to predict behavior, build new molecules, and troubleshoot when unexpected things happen. I’ve taught undergraduates who felt lost in a sea of chemical structures, but breakthroughs came after drawing out the formulas—no substitutions or shortcuts, just honest-to-goodness problem solving on paper.
Open-access materials—textbooks, online lectures, and databases—help learners and professionals check their work. Encouraging interactive workshops or pairing students up with those already working in labs can bridge the gap between theory and practice. Chemicals like 1-Propanesulfonic acid might remain behind the scenes, but knowing their precise formula reinforces the value of doing science with care and accuracy, one atom at a time.
Mentioning a chemical with a mouthful of a name like 1-propanesulfonic acid often raises concerns. People hear the word “acid,” and images of corroded pipes and safety goggles flash up. The way I see things, caution never hurts, especially around strong chemicals. Companies and labs use all sorts of acids every day. You learn over time that not every acid spells doom, but every one deserves respect.
1-Propanesulfonic acid does what most acids do: it can cause burns if it splashes on skin, and it stings like fury if it gets into your eyes. The safety data sheets spell out the immediate effects—irritation, redness, pain. I remember a splash of a less aggressive acid on my arm years back, and it left a mark for days. That’s just the start—imagine something a bit more persistent like this one when handled carelessly.
A person might sniff this chemical during handling. Even if it doesn’t smell strong, inhaling vapors of any acidic compound risks irritation in the nose and throat. Lab workers wearing gloves and goggles aren’t just following rules out of habit. These barriers keep skin and eyes protected from nasty surprises. I’ve fussed plenty over leaky bottles in storage. Just a little spillage ruins more than a mood—it threatens safety.
The real worry with many acids lands on toxicity. Science points out that 1-propanesulfonic acid acts more as a corrosive than a classic poison. It’s not considered acutely toxic to a degree that brings immediate systemic problems with low-level contact. But repeated exposure could set up a person for sensitization or chronic irritation. Prolonged exposure isn’t something to experiment with—respiratory and skin problems creep up in folks who don’t take care around chemicals for years.
Compared with more notorious compounds, 1-propanesulfonic acid doesn’t get flagged for high toxicity. Still, the argument for gloves, goggles, and a chemical hood holds up each and every time. Waste handling matters too—down the drain isn’t an option. Guidelines for hazardous waste come from hard-won experience, not just paperwork.
Beyond personal safety, thinking about what happens to these chemicals after use is key. Unchecked disposal can stress local water systems, and even a mild acid like this one can shift soil or stream chemistry in the wrong direction. I’ve watched smaller labs skip steps, thinking small amounts don’t count. But building up over time, even seemingly minor waste streams harm the environment and public health.
Regulations exist for a reason. They force a hard look at how chemicals move from jug to jar to waste barrel. Following these rules prevents a headache of fines and, much more importantly, keeps people and the planet healthy. Safety and environmental stewardship go hand in hand.
If you work with substances like 1-propanesulfonic acid, training goes miles further than guesswork. Protective gear keeps exposure low. Engineers design modern labs with ventilation in mind, and those choices pay off every day with lower risks. I’ve found that reporting near-misses and sharing the lessons keeps everyone sharper, too. Education and preparation are strong lines of defense.
Respect for any chemical, regardless of its hazard category, underlies safe work. Good habits multiply over time and help contain the potential dangers of everyday chemistry. Staying alert and responsible keeps the routine from turning into a regrettable story.
1-Propanesulfonic acid doesn’t get much attention outside chemistry circles, but its presence in some labs and production sites calls for respect. This isn’t just about following the printed storage instructions and checking a few boxes. People working with chemicals know accidents rarely care about paperwork—they thrive in clutter, forgetfulness, and loose lids. This acid is no slouch. It’s corrosive and loves to draw water from the air, which can create hazards for skin, lungs, and equipment. Getting splashed isn’t just uncomfortable, it could mean burns and ruined gear.
Experience teaches that even seasoned workers get careless when shelves get crowded or jobs pile up. Failing to keep 1-Propanesulfonic acid tightly closed and away from moisture has consequences. If this acid soaks up water from humid air, it can change strength and start breaking down containers over time. Metal shelving, especially, suffers from slow corrosion that might not look serious at first. Months pass, and suddenly you’re dealing with pitted racks or odd-smelling leaks.
Big glass jars or heavy-duty high-density polyethylene bottles do the job. After opening, folks should wipe the rim and make sure the cap goes back on straight. I’ve seen leaking bottles turn into a sticky mess on the bench, attracting dust and damaging notes taped to jars nearby. A dry, cool storage room makes things easier. Heat speeds up reactions you don’t want, so air conditioning in chemical storage pays for itself by lowering the chance of surprises.
Safe storage sometimes goes out the window when space feels tight. Temptation grows to tuck acids closer to unrelated substances, just for convenience. Mixing up shelves with strong bases or oxidizers brings a gamble few can afford. One dropped bottle or cracked cap, and those chemicals might interact in ways that endanger health and cut deeply into budgets due to lost material and cleanup.
Smart labs paint shelving or label cabinets by chemical type, so nothing acidic ends up near something that will react dangerously. It only takes one slip of the hand during a busy day to set off a chain reaction. I once worked next to someone who accidentally stored a strong acid next to hypochlorite—the vapor that drifted out led to panicked evacuation and a week lost out of the schedule.
Seriousness about 1-Propanesulfonic acid comes from real stories and honest mistakes. Every storage decision should aim to prevent today’s little shortcuts from leading to tomorrow’s big accidents. Keep inventory tight, labeling clear, and don’t let old containers stack up. Rotating stock, like rotating food in a fridge, means nothing gets too old, brittle, or forgotten.
Access controls—like locked cabinets or supervised storage—help limit exposure to those who understand the risk. Training new workers to spot early warning signs, such as cloudiness in the bottle, sticky residue, or odd odors, stops many incidents before they start. Trust in the system grows as people see the sense and safety in sticking to a routine that respects every chemical for what it is. One good habit makes room for another, and injuries start to fade from memory.
Regulations from authorities like OSHA exist for a reason, but the real safety comes from people refusing to rush and always double-checking their work. Safety beats speed every day of the week, especially with something as unforgiving as 1-Propanesulfonic acid.
I’ve seen a lot of exotic compounds come up in chemistry talks and applied projects, but 1-Propanesulfonic Acid might not sound familiar unless someone has spent time in a lab or on a plant floor. This humble organosulfonic acid, though, does a lot of heavy lifting in several industries.
Its workhorse reputation begins in organic synthesis. Chemists lean on 1-Propanesulfonic Acid for its strong acid properties and its ability to help shape reactions, especially in the making of pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals. As a catalyst, it gets reactions moving faster and cleaner. Compared to old staples like sulfuric acid, it's less aggressive towards glassware and easier to rinse away once a reaction wraps up.
In one project I worked on, sulfonic acids played a pivotal role in ensuring a critical step in molecule building finished on time and under budget. Efficiency, reliability, cleaner end products—these matter to both researchers and manufacturers.
The electroplating world leans on chemicals that bring conductivity and stability to their baths. 1-Propanesulfonic Acid is a popular electrolyte additive, making it easier for metals like nickel and copper to spread evenly over surfaces. This leads to higher-quality finishes for electronics parts, automotive components, and even jewelry.
Consistency keeps production lines running, and plating solutions containing this acid give more manageable results compared to some harsher alternatives.
Medicinal chemistry sees real benefits from propanesulfonic acid. During the development of some drugs, scientists use it to tweak solubility or modify the behavior of other compounds. It acts as a supporting player, helping get better yields and new pharmaceutical scaffolds to market. Safety and accuracy count, especially when a drug project transitions from the lab bench to pilot scale.
Chromatography labs also keep it handy for use as an ion-pairing agent. In complex separations where details matter—like tracking chemical impurities in drug batches—adding this acid helps scientists find what they’re looking for faster and with better resolution.
Making specialty polymers sometimes takes more than just clever monomers; you also need the right additives. 1-Propanesulfonic Acid supports the polymerization of tough-to-handle monomers or acts as a functional group when tweaking polymer properties, like conductivity or binding strength. The acid group sticks well, so once it’s in the chain, performance boosts show up in finished plastics, coatings, and elastomers.
It’s no stranger to the world of cleaning, either. In commercial cleaners and some home products, its acidic punch breaks down mineral scale or stubborn dirt, especially on surfaces that would corrode under harsher acids. Safe handling remains vital, but workers appreciate not having to mask up for fumes or worry about pitted equipment after routine washes.
1-Propanesulfonic Acid might not command headlines, but its versatility keeps it valuable. From speeding up chemistry to perfecting coatings and helping deliver safer pharmaceuticals, it underpins a lot of progress behind the scenes. Better safety data, greener manufacturing processes, and smarter handling can help extend its reach even further, helping industries get the reliability they need without cutting corners on health and safety.
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 3-Sulfopropanoic acid |
| Other names |
1-Propanesulphonic acid Propanesulfonic acid n-Propylsulfonic acid Propylsulfonic acid 1-Propylsulfonic acid PSA |
| Pronunciation | /ˈwʌn-proʊˈpeɪnˌsʌlˈfɒnɪk ˈæsɪd/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 1120-71-4 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1720241 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:42697 |
| ChEMBL | CHEBI:4482 |
| ChemSpider | 12654 |
| DrugBank | DB01944 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 05a926b5-ffd1-4cc3-8870-7be06aacd6e1 |
| EC Number | 214-317-9 |
| Gmelin Reference | 80315 |
| KEGG | C01051 |
| MeSH | D011369 |
| PubChem CID | 8739 |
| RTECS number | TY5250000 |
| UNII | 7O8F93P8PO |
| UN number | UN3265 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID9020667 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C3H8O3S |
| Molar mass | 122.17 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid. |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.269 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Soluble in water |
| log P | -1.0 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0065 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.53 |
| Basicity (pKb) | -5.7 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -54.5×10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.404 |
| Viscosity | 1.543 mPa·s (25 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 2.64 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 190.9 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -694.6 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | −1814.3 kJ·mol⁻¹ |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive, causes severe skin burns and eye damage, harmful if swallowed, may cause respiratory irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS05 |
| Pictograms | GHS05,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage. |
| Precautionary statements | P264, P280, P301+P312, P330, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 3-0-1 |
| Flash point | 129 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 oral rat 1780 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral rat LD50 = 2,453 mg/kg |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL: Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | REL: NIOSH 1 ppm (6 mg/m³) |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | IDLH: Not established |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Methanesulfonic acid Benzenesulfonic acid 1-Butanesulfonic acid |