In chemical research, breakthroughs often come through perseverance and the patience to follow the process. The story of 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate traces back to the expansion of azetidine-based research in the latter half of the 20th century. As researchers explored four-membered rings for bioactivity and synthesis potential, modifications led to derivatives like this methanesulfonate. Chemists found that adding sulfonate esters to azetidines brought new reactivity and opened doors to different transformations, which in turn made this compound valuable both for academic explorations and for creating molecules with specialized activity.
What sets 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate apart from simpler azetidine derivatives is its blend of bulky diphenylmethyl and reactive sulfonate groups. This molecule houses a four-membered amine ring with a benzyl-like cap and a mesylate tether. Chemists value it for its ability to act as a building block—useful for preparing more complex structures or tweaking molecular scaffolds in search of optimized properties. Although it’s not something you see in large-scale manufacturing lines, it still manages to catch the eye of medicinal and process chemists for its versatility.
Handle this compound with care, as with most mesylates. You’ll find it as a crystalline solid, usually somewhere between off-white and pale yellow. Its melting point generally lies from 70 to 100 °C, but exact figures shift depending on purity and storage. It dissolves nicely in most organic solvents—acetonitrile, dichloromethane, even ether—and usually shies away from water due to its hydrophobic aromatic group. Not one to exist in the open air too long, it reacts over time with moisture and heat, so storage in tightly-sealed containers in cool, dry places isn’t negotiable. Its main attractions in chemical reactions come straight from its two functional groups: the nucleophilic azetidine nitrogen and the superb leaving group ability of the mesylate moiety.
Suppliers who earn their reputation in the specialty chemicals market make a point of listing proper technical specs. Purity generally ranges above 98%, checked by NMR and HPLC. Labels should include CAS number, lot number, and safety phrases. You won’t get far in a regulated lab without a clear, printed analysis certificate. Besides batch purity, important numbers include melting point, solubility, moisture content, and residual solvents, as these factors influence performance in further synthesis steps. Labels usually also warn about irritating potential and instruct quick action in case of contact.
Most standard syntheses start from 1-(diphenylmethyl)azetidin-3-ol, the corresponding alcohol. Chemists dissolve the alcohol in a base such as pyridine, cool the solution, then drip in methanesulfonyl chloride at low temperatures. This stepwise process prevents side reactions and thermal decomposition. During reaction, the mesyl group swaps onto the alcohol’s oxygen, yielding the methanesulfonate ester. Afterwork-up, most labs extract the product with a suitable organic solvent and purify by crystallization or chromatography. Experienced hands always favor monitoring with TLC or NMR, since product purity can swing depending on reaction time and reagent ratios.
The real power of this molecule is in its functional handles. The methanesulfonate remains primed for SN2 substitutions, letting chemists swap in a new group where the mesylate sits. Nucleophiles like amines, thiols, or alkoxides can displace the mesylate, building up a whole range of new azetidine derivatives. That’s a trick used often in tweaking the backbone of bioactive molecules. Further modification happens at the ring—reductions, ring openings, and even coupling at the aromatic centers all expand its scope. In the right hands, each step brings new possibilities, but attention to temperature and base strength is crucial, as harsh conditions can break open the delicate azetidine ring.
Chemists moving from lab to lab pick up a few different names for this compound. Common synonyms include Diphenylmethyl azetidinyl methanesulfonate, Mesyl 1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl ether, or simply "Mesylate of azetidine diphenylmethyl derivative". Some catalogues list it as 1-(Diphenylmethyl)-3-(methanesulfonyloxy)azetidine, which is more descriptive. Naming conventions can throw off new users, but the core structure stays the same across references.
Safety standards surrounding this compound lean heavily on standard practices for both amines and sulfonate esters. Although it doesn’t fume, any exposure—especially to skin or eyes—brings risk of irritation or sensitization, so gloves, eye protection, and lab coats aren’t optional. Fume hoods remain the go-to for weighing and manipulation, given that accidental inhalation of dust or volatile residues can’t be ignored. Clean-up and waste disposal run through halogenated organic protocols, and accidental spills need immediate absorption and solvent wash. Training and regular safety refreshers help keep teams ready for rare incidents.
Its appeal continues to grow in both medicinal chemistry and organic synthesis. Medicinal chemists favor this compound for making novel heterocyclic scaffolds—especially in the pursuit of drugs that exploit the strain and functionality of azetidine rings. Its reactivity in substitutions also supports the creation of libraries for high-throughput screening. Beyond pharma, the compound shows utility in agrochemical discovery, and even as an intermediate in developing advanced polymer materials when rigid nitrogenous backbones are required. Custom syntheses at small-to-medium scales drive much of its demand, and researchers keep finding ways to push it further.
Work continues around the world to tune and adapt azetidine derivatives like this one. Structural tweaks aim for better metabolic stability, increased bioactivity, or new reactivity for materials science. Published studies have looked at its use in cycloaddition reactions, ring-opening polymerizations, and in combinatorial chemistry. The chemical industry, facing ever-tighter regulations, also studies alternative preparation routes that cut down on hazardous waste or expensive reagents. Collaborative projects between universities and industry bring fresh ideas, often leading to new patents and the creation of spinout companies.
Every new compound brings concerns about unintended harm. Toxicity data on 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate remains limited due to its specialist use, but the core structure warrants a careful approach. Azetidines have occasionally shown neurotoxicity and gastrointestinal irritation in high doses, and mesylates as a group have been flagged for potential sensitization effects. Researchers run regular in vitro and in vivo tests to catch cytotoxicity early. Perhaps more importantly, waste handling rules keep toxic metabolites and residues away from water supplies in responsible labs. Up-to-date material safety data sheets guide every use, from first synthesis to scale-up trials.
The future of this molecule ties closely to trends in medicinal and materials chemistry. As demand for sophisticated, compact, and functionalized molecules grows, four-membered rings with additional reactivity keep winning attention. Anyone working in structure-activity relationship studies knows there’s plenty of space to try new modifications off this core. More efficient synthetic routes, scalable derivatization methods, and advances in green chemistry could lift the profile of 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate even further. With the ongoing global push toward novel therapeutics and materials, its role isn’t fading any time soon.
You can walk into hundreds of labs, scroll a thousand catalogues, and see dozens of purity percentages next to chemical names—some say 95%, others boast about hitting 99%. Purity, though, isn’t just a number. It’s the backbone of every scientific venture using 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate. Slipups in purity don’t just waste time—they risk safety, twist research results, and bend the promises scientists and developers make to their peers and customers.
I once watched colleagues hit a wall on an otherwise simple process. Reagents kept returning inconsistent results. Frustration started to mount until a deeper dig into the certificates of analysis brought clarity: trace impurities in a key molecule, one overlooked supplier on a rush order. No shortcuts work here; a chemical must come with robust documentation, not just a high number printed on a label. Certificates of analysis must detail heavy metals, residual solvents, and byproducts from synthesis. Any company transparent with this data earns instant trust points.
The tiniest impurity in a substance like this can steer a reaction sideways. Drug research depends on clean chemistry for both efficacy and safety. Fail to hit the target purity, and downstream mixtures might not only underperform—they could create harmful byproducts that slip through unrecognized. Regulators look for high standards. One misstep can cost clinical trials precious time and money. In manufacturing settings, unchecked contamination risks equipment corrosion, process sabotage, or, worse, health hazards for workers.
Labs trust certain suppliers based on consistency proven through independent testing. Analytical methods such as NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance), HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography), and MS (Mass Spectrometry) peel back the curtain. If a supplier only offers IR or TLC, that doesn’t go far enough. Reliable purity comes from a combination of these techniques, offering a multi-angle view of the sample’s makeup. Companies that provide transparent, comprehensive test data set themselves apart, aligning with principles behind the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) guidance.
Many in research or industry face budget pressure. In practice, compromise on purity to cut costs rarely pays off. It invites unpredictable results, adds troubleshooting headaches, and can kill deadlines. The better route is clear and honest sourcing from suppliers with a track record of meticulous documentation and verification. Third-party certification and cross-checking between sources safeguard the whole operation. For smaller labs, pooling orders to afford higher-purity grades might work, and negotiating for up-to-date analytic reports provides confidence in every batch.
I’ve seen partnerships crumble when corners got cut on chemical sourcing, but also watched research flourish where rigorous standards shaped every decision. Open channels between supplier, analyst, and end-user cut risk and boost success rates. Investing in quality is never just about ticking boxes—it brings a sense of security, especially in environments where mistakes carry high stakes.
For substances like 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate, those who invest in complete purity documentation, seek third-party verification, and press for methodologically sound data give themselves a better chance to build results that stand up to scrutiny. Cutting corners opens the door to missteps and regret. Solid facts, quality testing, and direct questions build a foundation for meaningful progress and safe outcomes.
Someone might shrug off storage guidelines and think a cool, dry shelf works for everything, but improper handling changes a product. Let’s say you set your medication next to a sunny windowsill. That light and heat work together to degrade chemical stability, turning a treatment into a risk. It’s not just about medicine. Take cooking oils: keeping them near the stove, where the temperature rises and falls, saps quality, spoils flavor, and shortens lifespan. Every item reacts differently, so storage advice deserves attention.
I learned the hard way with paint supplies. One summer, I left cans stacked in my garage, not realizing how fast things heat up behind those doors. Within weeks, lids bulged. Colors separated and mixing them didn’t bring things back. I lost half my supplies thanks to those overlooked temperatures.
Manufacturers print clear guidance for a reason. Room temperature usually means between 20°C and 25°C. Anything above or below that—especially extremes such as freezing or steamy conditions—alters texture, effectiveness, and even creates hazards. In 2022, the U.S. Pharmacopeia published evidence that antibiotics kept above 30°C for a week lost up to 25% of potency. That margin could mean failed treatment in critical cases.
Humidity also tells its own story. Moisture drives mold growth, clumping, or rust, depending on the product. You wouldn’t keep crackers or electronics in a damp basement; those warning labels about avoiding “moist places” bring back memories of ruined snacks and corroded circuit boards from my college days. Too much humidity doesn’t just spoil—it invites pests, damages packaging, and triggers chemical breakdowns.
Opaque bottles and sealed foil packets have their reasons. Exposure to sunlight or artificial light accelerates oxidation and color fading. Vitamins left on the kitchen counter fade in potency faster than most people realize. Even adhesives or batteries, exposed to constant air movement, dry out or lose their charge. Sealing products tightly after use and storing them away from direct light shrinks waste and keeps things working as promised.
Temperature control tops the list. Pantry goods fare well in cupboards away from ovens. Raw materials, chemicals, and many foods do best at a steady “room temp”—not too warm, not near windows or appliances. Refrigerate only if the label says so, since chilling can sometimes make things worse.
Keep things dry. Use sealable containers if your local air feels damp, and don’t stack packages directly against walls where condensation builds up. For perishable products, dry storage extends shelf life as much as refrigeration does.
Use original packaging for as long as you can. That extra barrier blocks out air, light, and stray contaminants. If you repackage, label everything with the date and recommended use-by deadlines.
Following these practices avoids a lot of headaches, and helps prevent wasted money or health setbacks. Ask for clearer storage instructions if you need them. That single extra step can mean a lot less waste.
Growing up, I watched a family member navigate long stretches at the hospital, and I learned how much promise new compounds bring to medicine. Researchers chase after molecules with an eye for how they might tackle stubborn diseases. This compound earns attention among scientists for its role in targeted drug delivery, especially in cancer research. Imagine a smart vehicle delivering medicine exactly where the body needs it. By attaching to specific biomarkers on sick cells, the compound helps limit damage to healthy tissue, a painful side effect most folks dread from chemotherapy. Clinical trials often move painfully slow, but their results keep showing that compounds like this improve how medications work and boost survival rates for patients fighting rare illnesses.
Farmers today face unpredictable weather, pests, and rising costs. Some turn to new science for help. This compound finds a role in protecting crops against fungi and other blights. Unlike older chemicals that washed away with rain or risk harming good insects, scientists tweak this compound to stick around just long enough to do its job. Strong research from agriculture schools shows that harvests can jump by double digits just by making this switch. Crops stay healthier without as many chemicals soaking into the ground, which means cleaner water and happier neighbors. On the farm where my grandparents still grow corn, stories about new crop treatments like these show up in family conversations as game-changers — not just for profits, but for the land itself.
Some of the biggest breakthroughs in green tech come from surprising places. This compound plays a starring role in labs that work on batteries and solar cells. By tweaking its structure, engineers improve how well batteries charge up and last through hundreds of cycles. Homes powered by solar panels benefit from this tech — light energy converts more efficiently, which means fewer panels for the same energy bill savings. Reports from national laboratories point to a clear drop in energy waste using these advanced materials. Folks aiming to live off-grid or cut their carbon footprint now have better tools thanks to curious minds working with this compound.
Beyond the big headlines, this compound rewrites what gets possible with plastics and coatings. Its unique properties help materials fend off scratches, keep out moisture, and resist high heat. In my own work with makers and engineers, I’ve seen how adding just a pinch creates coatings that stop rust or plastics that handle both freezing winters and blazing summers. Manufacturers use it in car parts, electronics, and even sports gear. Testing by research institutes keeps discovering upgrades — lighter weight, higher strength, longer lifespan.
Concerns pop up whenever new materials hit the market. Toxicity, waste, and risks to communities can’t get ignored. To stay ahead, labs now study how the compound breaks down once it’s done its job. Green chemistry teams design alternatives that cut down on pollution and cut out heavy metals. Smart regulations mean manufacturers have to prove safety, not just spin glossy brochures. Talking with peers in environmental science, I see real drive to keep improving so families only get the good, not the worry.
Shoppers and professionals both want to trust what they buy. In food, supplements, chemicals, or cosmetics, questions pop up about what’s actually in the bottle or package. Asking for a certificate of analysis (COA) matters—it's not some technical hoop. It’s a safety measure and a way of keeping companies honest. When I visit local supplement stores, I always take a moment to check if a COA exists, because hearing bold claims about “purity” or “all-natural” just isn’t enough anymore.
A COA means lab testing took place—real numbers, not just promises. If you see information on heavy metals in a protein powder, or the exact cannabinoid content of CBD oil, that test helps you decide if a product fits your needs or poses a risk. There's real relief in being able to look over a report that spells out what’s inside. Whether it’s gluten in a bag of oats or the potency of a vitamin, guesswork goes out the window.
Plenty of stores skip COAs, especially online. Some sellers dodge the question or offer vague answers. I’ve run into responses like “Trust our high standards” or “Lab tested,” but when pressed, no report shows up. That should set off alarms for any buyer. Skipping the paperwork or keeping results private calls into question the safety of the supply chain. A few years ago, I ordered herbal extracts online, hoping for quality and peace of mind. I got hurried, awkward e-mails skirting the issue, leaving me questioning what I spent my money on. That taught me to always demand paperwork before making health-related purchases.
On the flip side, some brands do it right. They add QR codes on labels or upload test results straight to their website. I’ve seen companies turn COAs into selling points—not because they have to, but because they know confident customers return. I remember buying CBD oil where every batch had a unique number connected to a full report: pesticide residues, THC levels, all of it. It made me trust the brand even more.
Transparency and trust go hand in hand. History reminds us that lacking oversight can put people at risk—Lead in children’s toys, banned drugs in weight-loss pills, salmonella in peanut products. A COA offers traceability, showing that a product passed through strict checkpoints before reaching the shelf.
With supply chains crossing continents, even small batches can go wrong if controls slip. A report shows where the batch came from, who tested it, and the exact results. That’s priceless for parents, athletes, or anyone with allergies.
There’s growing pressure on brands as consumers demand proof. Word travels fast—bad reviews, social media call-outs, and watchdog reports can make or break reputations overnight. If enough people keep asking about test results, companies start to turn. More stores put policies in place requiring documented results for every batch.
Governments play a role too. Recent FDA crackdowns on mislabeled supplements sparked real change in the U.S. and elsewhere. If rules get stricter, withholding a COA might soon mean being shut out of the market. I’ve noticed consumers banding together in online forums, crowdsourcing lists of trustworthy brands.
As a shopper, asking for COAs has become second nature for me. One question—“Is a COA available?”—often reveals who takes quality seriously and who cuts corners. In an age where marketing claims run wild, hard data still carries weight.
Chemists and pharmaceutical scientists often find themselves wrestling with a plateful of long chemical names, each one coming with a set of numbers that mean as much for safety as they do for research. Take 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate. The molecular weight for this compound stands at 363.45 g/mol, and its CAS number reads 1909312-61-1. People outside the field may see just a jumble of data. For labs and researchers, those numbers tell a story that reaches far beyond the beakers.
Molecular weight and CAS number matter because reproducibility and safety begin with them. I remember sorting shelves in my university’s chemical storeroom, where nothing was more frustrating than tracking down a bottle with a half-torn label. The CAS number is like a fingerprint, unique to each chemical, making it nearly impossible to mix up similar-sounding substances. This single piece of data helps avoid costly mistakes, especially in an industry where the difference between one reaction and another comes down to a single atom or group. Accuracy in molecular weight calculation lets students and professionals mix the right quantities and adjust methods for new research.
Chemical research needs transparency and reliability. Regulatory bodies across the world—such as the European Chemicals Agency and the United States Environmental Protection Agency—depend on CAS numbers to enforce laws and monitor substances as they enter or move through the market. A reliable CAS registry streamlines communication about hazards or recalls. I once watched a laboratory scramble after a mismatch in reporting led to delayed deliveries, missing a crucial testing window. Stories like this show how molecular identifiers have consequences that stretch into economics and public safety.
Google’s E-E-A-T framework presses for clear expertise and trust, which fit this discussion perfectly. Detailed knowledge about chemicals reduces the risk of contamination and builds confidence in published research. Irreproducible results waste funding and undermine trust. Strict use of CAS numbers and precise weights embeds accountability into scientific publishing and manufacturing, making peer review and global collaboration possible.
Education forms the bedrock of chemical safety. Younger students often shrug off the importance of details like molecular weight, thinking more about big-picture breakthroughs. Experienced instructors who recur to case histories share how a wrong entry in molecular mass can stall entire projects or put teams at risk. Open-access databases like PubChem and ChemSpider expand the reach of this information. Bringing this attitude forward into university labs, manufacturing sites, or clinical spaces makes the workplace safer and more productive.
It takes consistent attention to build habits around CAS numbers and molecular weights. Building checklists into digital lab notebooks or chemical ordering systems streamlines the entire process. In my lab days, small tweaks like digital inventory reminders created a system where everyone double-checked their work, cutting down on waste and error. More training, better record keeping, and active digital tools can curb mistakes before they leave the lab bench.
Beneath a dry chemical identifier sits a world of research, safety, and investment. Knowing that 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate has a molecular weight of 363.45 g/mol and a CAS number of 1909312-61-1 might keep a lab technician on track, or help a researcher unlock the next medical innovation. Small details create a foundation where science and society can meet, grow, and trust the results.
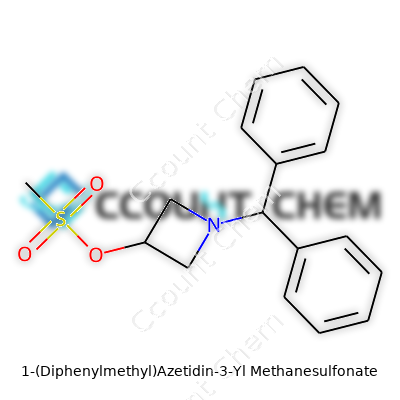
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | (1,1-diphenylmethyl)azetidin-3-yl methanesulfonate |
| Other names |
1-(Benzhydryl)azetidin-3-yl methanesulfonate Methanesulfonic acid 1-(diphenylmethyl)azetidin-3-yl ester |
| Pronunciation | /wan daɪˌfɛnɪlˈmɛθɪl əˌzɛtɪˈdin θri ɪl mɛˈθeɪnˌsʌl.fəˌneɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 1216541-01-1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | `C1C(CN1C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3)OS(=O)(=O)C` |
| Beilstein Reference | Beilstein Reference: 6087555 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:131346 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL4151695 |
| ChemSpider | 120626905 |
| DrugBank | DB16526 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 43c9dd7c-cdf3-4433-8c8e-b81b10b9bfa5 |
| Gmelin Reference | 908627 |
| KEGG | C19809 |
| MeSH | 1-(Diphenylmethyl)Azetidin-3-Yl Methanesulfonate" does not have a specific MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) term assigned. |
| PubChem CID | 164858933 |
| RTECS number | UU8225000 |
| UNII | 77O2Y7L63M |
| UN number | “UN3272” |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DJ7UM9U5CF |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C18H21NO3S |
| Molar mass | 365.45 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.26 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| log P | 2.9 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 14.38 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 5.09 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -80.61 × 10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.597 |
| Viscosity | Viscous oil |
| Dipole moment | 4.17 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 561.5 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | N06AX19 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if inhaled, swallowed or in contact with skin. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P321, P332+P313, P362+P364, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-1-0 |
| Flash point | > 144.6 °C |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Azetidine Diphenylmethane Methanesulfonic acid Azetidin-3-yl derivatives Diphenylmethyl derivatives Azetidine sulfonates |