Over the past few decades, the journey of 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt has reflected broader changes in the chemical industry. Early on, chemists focused on small-scale syntheses to explore new functional groups. This compound caught attention in the 1960s, as sulfonic acid derivatives became vital for separation techniques. Fast development in ion-exchange chromatography pushed research to better understand and optimize sodium salts with stable, predictable properties. Researchers leaned on these sulfonates to sharpen analytical methods, opening the door for widespread industrial and academic use. This background led to its current widespread application across laboratories around the world.
1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt usually appears as a white, crystalline or powdery substance, offering high solubility in water. The ionic nature of the sodium sulfonate makes it suitable for processes demanding conductivity and precise ionic strength. It's most widely stocked in bulk chemical suppliers and lab reagent catalogs, as it’s reliable and cost-effective. Over time, it has become a mainstay for anyone working on ion pair chromatography and analytical methods that depend on controlling charge interactions at a micro level. Its robustness even at modest temperatures and pH levels anchors its usefulness among researchers who need predictable chemical behavior.
With a molecular formula of C4H9NaO3S and a molar mass around 176.17 g/mol, this compound offers stable handling and transportation. The melting point usually sits above 250°C, so it doesn't break down or sublimate under common lab conditions. In water, it forms clear, conductive solutions that help maintain ionic conditions in separations or reactions. Its sulfonate group guarantees strong acidity in solution, imparting properties that remain stable even in the presence of mild acids or bases. This reliability of dissociation is crucial during repeat procedures in analytical runs.
Manufacturers generally offer this compound at purities above 98%, as trace contamination can interfere with many chromatographic or synthesis roles. Labels list sodium content, moisture percentage, and batch origin. Common packaging involves moisture-proof containers, due to the compound's tendency to attract water from the air. Safety data sheets highlight chemical identification numbers and straightforward instructions for safe storage. Requirements from regulatory agencies, including the GHS, always demand labeling for eye irritation potential and procedures in case of accidental exposure. These details support safe, standardized use in both teaching and research labs.
The most popular production route starts with 1-Butanesulfonic acid, prepared through sulfonation of 1-butane with concentrated sulfur trioxide. After isolating the acid, neutralization with sodium hydroxide converts it to its sodium salt. The product typically goes through recrystallization to remove byproducts and unreacted materials. Practical production scales up easily since the steps use common reagents and equipment. Careful control over pH and temperature keeps yields high and impurity levels low, matching the needs of academic and industrial end users.
Chemists value the sodium salt for its resilience, but they use it as both a starting point and a buffer in more advanced reactions. It takes part in nucleophilic substitutions, especially where the sulfonate serves as a leaving group. Its minimal reactivity towards oxidants and reductants means labs use it to maintain consistent ionic backgrounds, avoiding unwanted side reactions. Under some conditions, it can act as a phase transfer catalyst or help mediate metal ion reactions. In personal experience with HPLC method setups, replacing other alkyl sulfonates with this compound improved reproducibility and peak shape for several basic pharmaceuticals.
Chemists often encounter this compound under several synonyms. Common names floating around academic papers and catalogs include Sodium Butanesulfonate, 1-Butanesulfonic Acid, Sodium Salt, N-Butylsulfonic Acid Sodium Salt, and Butane-1-sulfonic acid sodium salt. CAS numbers used for ordering and regulatory purposes: 2386-54-1. These synonyms keep product sourcing straightforward for anyone shopping from international suppliers or regulatory lists.
Handling 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt in university and industry labs rarely causes safety incidents, provided users respect the substance’s basic irritant properties. Accidental skin or eye exposure gets managed with copious rinsing and basic first-aid. No explosive, flammable, or highly toxic attributes show up under normal use. For workplace safety, common personal protective equipment such as goggles, gloves, and dust masks covers typical exposure scenarios. Facilities keep it away from food and incompatible chemicals. Emergency instructions on product data sheets remain easy to follow even for new lab workers.
In chromatography labs, this sodium salt shapes ion pair and ion exchange methods for analyzing everything from amino acids to pharmaceuticals. It allows fine-tuning of elution, critical for separating structurally similar compounds. Outside analytical chemistry, it supports pharmaceutical manufacturing as an intermediate, particularly in forms where sulfonate groups boost solubility. In water treatment, it helps regulate system conductivity and monitor processes involving sulfonated contaminants. From teaching settings to pharmaceutical quality control labs, technicians reach for this compound to deliver consistent outcomes.
Growth in use keeps pace with the push for faster, more sensitive chemical analyses. As research races ahead in personalized medicine and complex mixtures, demand for tighter control over separation conditions has spurred refinements in both the purity and particle size distribution of this compound. Researchers studying protein and peptide separation often design whole workflows around 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt, seeking sharper columns and better signal-to-noise ratios. Advances in mixture analysis—especially for large biological molecules—draw heavily on this salt as an experimental building block.
Most animal and environmental toxicology reports peg 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt as a mild irritant, not a major hazard. LD50 values in rodents suggest low acute toxicity, with symptoms limited to gastrointestinal discomfort at excessive doses. Standard environmental fate studies note high water solubility and moderate persistence. Researchers examining aquatic impacts recommend close monitoring, especially since highly sulfonated compounds sometimes resist standard wastewater treatment. Proper disposal protocols push for dilution and processing through authorized chemical waste streams, not regular drains, to limit any long-term risk to aquatic environments.
Emerging interest in green chemistry could shape future production and purification, as sustainability gains a stronger role in procurement and waste management. Next-generation chromatographic techniques, already demanding cleaner and more tailored reagents, may prompt manufacturers to tighten controls on heavy metal or organic contaminants in the sodium salt. Collaborations among universities, industry, and regulatory groups will likely develop best practice guides for safe handling and greener manufacturing. Given its proven track record, there’s every reason to expect continued expansion in both academic and applied settings, especially as bioanalytical needs keep growing.
Most people never hear about 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt outside of a lab, but this white, crystalline salt actually shapes things in the chemical and pharmaceutical world. With the formula C4H9SO3Na, it often shows up behind the scenes in many research and production settings. It's water-soluble and carries a strong acidic punch, making it more than a shelf chemical—it sets the tempo for specific reactions.
Scientists and technicians cling to reliability in analysis. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) takes center stage in this field, and 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt gets used as an ion-pairing agent. Forget jargon—here’s why that matters: HPLC separates, identifies, and quantifies components in mixtures, and this salt keeps certain molecules visible during the test. Other agents struggle with some stubborn pieces, but this one grabs onto charged molecules, allowing for more precise measurement. Companies testing water quality and drug development teams lean hard on this edge.
Making any drug brings strict rules, whether it’s aspirin or a breakthrough treatment. Pure substances make or break safe medicines. 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt sweeps through as a reagent, helping chemistry teams clean up compounds during drug synthesis. I remember a chemistry student in my university days mentioning how this salt cut time spent hunting impurities in their sample prep. Fewer impurities mean more dependable results, and ultimately, a safer final product.
Versatility stands out with this compound. Besides HPLC, research labs handle this salt for titration and pH control, adjusting environments in test tubes to just the right conditions. It supports consistent testing conditions by balancing the mixture, maintaining stable pH, and helping scientists repeat results—science leans on repeatability as much as discovery. This consistency helps scientists from academic labs to private industry validate their findings.
Lab teams in food safety and environmental analysis also find this salt handy. It acts as a buffer or helps separate ingredients in everything from water tests to food contamination checks. Think about how food recalls rely on accurate data. The chemistry behind those results often owes a debt to chemicals like this. As regulations push for cleaner water and safer food, dependable reagents help make those standards realistic.
Responsible science means clear labelling and safe usage. Suppliers follow labeling, storage, and safety protocols that keep teams informed. Material Safety Data Sheets spell out risks—direct skin contact, inhalation—and guide on spills or exposures. In a world that sees more chemicals transported across borders, this matters for long-term health of workers and end users.
Some chemicals leave behind waste that’s tough to manage or recycle. Researchers keep searching for purer, more sustainable alternatives where they can. As labs face stricter environmental laws, green chemistry guides chemical selection. Until then, handling and disposal rules offer some control over risks tied to 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt.
Anyone who works with chemicals has a responsibility to keep both people and products safe. 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt doesn’t always get flashy headlines like other substances, but that doesn’t make its handling less important. My own time logging inventory at a research lab taught me that small details in storing these types of chemicals can impact both research results and lab safety. Poor storage practices not only risk wasted money but also threaten the well-being of everyone nearby.
This compound prefers a dry place, out of direct sunlight, at a temperature between 15°C and 30°C. Cooler isn’t always better. Freezing temperatures can draw in moisture when you open the container, and humidity disrupts stability. I’ve seen how even minor lapses—like a cracked seal—draw humidity that quickly turns a fine powder into hard lumps. Keeping it tightly closed in a well-ventilated, low-moisture environment goes a long way.
Containers with a screw cap and desiccant help to block humidity. Labs running HPLC methods often store it in amber glass bottles, not just to reduce light exposure but for a physical reminder that the material needs thoughtful handling. If you have ever watched a chemical degrade after sitting near a sunny window, you learn the hard way how vital light protection is.
1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt reacts with strong oxidizers, so keeping it away from acids, peroxides, and bleach is common sense. Segregation matters. Grouping substances based on their risk cuts down on chances for unintended reactions, something I picked up sorting the old chemical storeroom in graduate school. Separate shelves, clearly labeled bins, and good ventilation help prevent unpleasant surprises.
Cross-contamination sneaks up in busy labs. Dust, spills, and even air currents can move small powders between jars. Using clean spatulas and never returning unused reagents to the main bottle protects quality. Double-checking labels and tracking expiration dates ensures accuracy in both research and production settings.
Gloves, goggles, and lab coats aren’t just for spill emergencies. Even routine handling exposes workers to contact hazards—especially if there’s skin moisture or if powder floats in the air. Spills can create slick floors or airborne dust, both of which risk accidents. In my early days, I saw a small unnoticed spill mushroom into a time-consuming cleanup that shut down half a lab for hours. Prompt attention and clear cleaning procedures make a difference.
Emergency spill kits and proper ventilation add another layer of protection. Even non-volatile salts like this one can still release dust. For people with allergies or respiratory issues, there’s no substitute for a well-maintained fume hood.
Following storage guidelines isn’t just bureaucracy—it's how scientists make sure experiments stay repeatable, and industry teams keep product specs tight. Simple steps like temperature logs and daily checks build a culture of trust, both for users and anyone downstream in supply chains. People learn best from real stories and hands-on sharing of good habits, not from dry lists or outdated safety posters.
Setting a strong example and holding each other accountable on storage practices keeps everyone safer and protects the quality of important work.
Solubility plays a big role in how chemists and industries approach a substance. In my time handling laboratory chemicals, I’ve come to appreciate how a compound’s solubility shapes everything from solution preparation to process design. Water, being one of the most universal solvents, sets a high bar in solubility expectations. This matters even more when the substance in question ends up in pharmaceuticals or other sensitive products, where efficiency and purity guide every step.
To figure out if 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt dissolves in water, it helps to look at its structure. This compound carries a sulfonic acid group, which often attracts water, and a sodium ion, which enhances water affinity. In practice, we see a trend with these types of salts: their ionic nature typically means they draw in water molecules with ease. Unlike long-chain hydrocarbons or other less polar substances, ionic compounds with sulfonate groups blend readily with water at room temperature.
From published solubility data, sodium salts of sulfonic acids show high solubility in water. Chemists recognize this class of compounds for their use as ion-pairing agents in liquid chromatography and other wet chemistry applications. The published works in the Journal of Chromatography and other peer-reviewed sources detail regular use of 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt in aqueous solutions across a range of concentrations. This experience matches my own time preparing buffer solutions, where the only limiting factor usually ended up being the solubility of the least water-friendly component—not the sodium salt.
High water solubility brings benefits: easy dosing, homogenous mixing, and reliable results during analysis or manufacturing. I’ve watched poorly dissolving reagents leave behind residue and spark troubleshooting sessions. Compounds like 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt avoid these headaches. Analysts and formulators benefit from quick dissolving powders that eliminate the need for complex preparation steps or organic solvents.
Unlike some highly soluble salts, 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt does not prompt widespread safety or environmental worries. The main point draws from routine lab handling instructions: always use gloves and eye protection, and flush any spills with a large volume of water. Questions sometimes pop up around environmental persistence, but sodium sulfonates are not among the major red-flag materials according to current safety databases.
Getting the most out of this compound starts with proper measurement and slow addition to water, stirring to avoid clumping. For users mixing large batches, using warm water helps speed things along without changing the salt’s basic properties. If cloudiness appears, it often clears up with a few extra minutes of stirring. For people formulating drugs or running chromatography tests, the high solubility speeds up workflow and sharpens precision. Researchers should still validate concentrations before scaling up, since impurities or pH changes sometimes affect dissolution rates.
Large-scale handling sometimes leads to caking or moisture uptake. Storing the sodium salt in airtight containers, away from humidity, keeps things trouble-free. Checking expiration dates ensures reliable behavior in critical methods. If a precipitate forms on storage, gentle warming or dilution usually restores clarity. If complete dissolution proves tricky, reviewing water purity or increasing agitation generally does the trick.
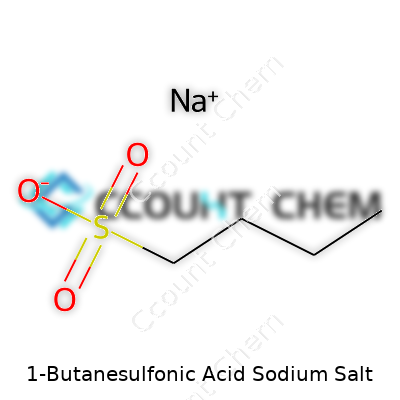
1-Butanesulfonic acid sodium salt has the chemical formula C4H9SO3Na. Getting this formula right means grasping how the molecule is built. There’s a four-carbon chain, sulfonic acid attached to one end, and sodium countering the acid group, making it a salt. It’s not just a random collection of letters—each part tells you something about how the compound behaves in real life.
The formula isn’t just for textbook trivia. In labs and industry, knowing this formula helps chemists avoid critical errors. For me, the first time mixing up sodium with potassium salts during a chromatography prep meant the entire separation flopped. Miss one element or add an atom in the formula, and you run into issues—wrong solution strength, unexpected reactions, or problems downstream.
1-Butanesulfonic acid sodium salt grabs attention in analytical chemistry. It pops up in ion-pairing for HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography), especially when separating tricky organic molecules. Some pharmaceutical labs lean on its consistent ionic properties to pull apart complex mixtures.
Looking at C4H9SO3Na gives more than structure. Sulfonic acid groups bring acidic tendencies, but sodium as a counter-ion calms things down. Understanding this blend helps recognize that the salt usually stays stable and water-soluble. In my own work, knowing I’m handling the sodium salt version, not the free acid, changes how I store, weigh, and dispose of leftover samples. Mix-up here can lead to lab hazards or environmental issues.
For those running commercial labs or pharmaceutical projects, formula certainty supports compliance with regulations. If you’re trying to meet standards set by agencies like the FDA or EPA, every atom matters. Auditors and inspectors won’t care about intentions—only what’s verified on paperwork. One time, a batch rejection resulted from a mislabeled surfactant ingredient; the source ended up being a mix of similar-looking sulfonate salts. Double-checking labels and MSDS sheets saves time, money, and reputation.
Mistakes around formulas often come from haste or copying old notes. I keep a habit of writing out full names with formulas whenever prepping a new solution. Teams benefit from digital logs where ingredients get checked by a second set of eyes. Simple steps like using barcodes on bottles and running IR or NMR checks on new shipments catch problems before they become disasters.
Better access to transparent chemical data reduces mix-ups. Resource sharing between academic groups and industry partners helps keep information fresh. Digital tools, including AI-driven chemical search engines, bring up-to-date, peer-reviewed chemical properties—so if a new staff member asks for the formula of 1-butanesulfonic acid sodium salt, they're not left guessing.
Getting the chemical formula right shapes outcomes in science and safety. It supports quality control, regulatory trust, and effective teamwork—surprisingly important for such a simple string of atoms and elements.
Spending a lot of time in labs, I’ve seen people work with all kinds of chemicals. 1-Butanesulfonic Acid Sodium Salt sounds straightforward, but any chemical can surprise you if you treat it lightly. This compound is usually found as a white powder, and it’s water-soluble. At first, it may not look dangerous, but skin and eye contact can irritate. Breathing in the dust isn’t healthy either. There’s a reason why even “normal-looking” lab salts always end up with safety sheets as thick as your palm. Accidents crop up quickly if people take shortcuts.
Gloves, goggles, and lab coats never go out of style around chemicals. It pays to remember that the skin absorbs all sorts of things people think just sit on the surface. A powder like this one can drift into the air or stick to your hands. Safety goggles protect your eyes from splashes, and gloves add an extra barrier that soap sometimes can’t beat. I always double-check that the gloves I use are meant for handling chemicals—as not all materials hold up equally.
Decades of handling lab chemicals taught me not to eat, drink, or touch my face while using reagents, no matter how clean they might look. Washing your hands before stepping out of the work area keeps you from carrying a problem home. An incident in my early years involved someone who forgot and ended up with a burn near their mouth. That stuck with me.
Proper airflow matters more than people admit. It’s not about paranoia but about real-world mistakes: an open powder bottle, a sneeze, and suddenly there’s dust in the air. I always make sure the workspace has a functioning fume hood or, if that’s not there, plenty of fresh air. Good airflow moves tiny particles away from your nose and mouth before they can cause harm.
Spills happen. My experience tells me that having a spill kit within arm’s reach can make or break a workday. For this compound, dry spills respond best to careful sweeping with minimal dust raising, no wild movements or rushing. Damp disposable towels pick up what’s left, and I use a neutral cleaner to mop the area. Running shoes track powder, so covering footwear or changing after an incident counts for a lot.
This salt stays stable in a cool, dry place, away from strong acids. Labeling every container clearly prevents mistakes, especially when powders look similar. I always store chemicals off the ground, keeping them above any risk of flooding or spills from other shelves.
The best protection in a work environment comes from everyone being on the same page. New staff deserve real training, not just a five-minute talk. I remember labs where casual attitudes led to confusion about which bottle contained which salt. Regular safety reviews, clear signage, and a culture of speaking up—these habits have saved more than one person from a costly mistake.
Safety is personal. Too many people treat chemical handling as a routine until something goes wrong. Looking after yourself and those around you takes more than just following rules; it’s about building habits that keep small errors from turning serious. Experience, respect for the material, and speaking up—these always pay off.

| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | sodium butane-1-sulfonate |
| Other names |
Sodium butanesulfonate Sodium 1-butanesulfonate Butanesulfonic acid sodium salt Sodium n-butanesulfonate |
| Pronunciation | /ˈwʌn.bjuːˌteɪn.sʌlˈfɒn.ɪk ˈæs.ɪd ˈsoʊ.di.əm sɔːlt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 2386-54-1 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1207930 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:63693 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL267661 |
| ChemSpider | 23741671 |
| DrugBank | DB04356 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.266 |
| EC Number | 262-119-7 |
| Gmelin Reference | 82858 |
| KEGG | C01888 |
| MeSH | D017978 |
| PubChem CID | 23665745 |
| RTECS number | YD0350000 |
| UNII | YD1YCT58PY |
| UN number | UN2817 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | OVS5Q6R8WL |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H9NaO3S |
| Molar mass | 180.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Soluble in water |
| log P | -2.0 |
| Acidity (pKa) | -2.1 |
| Basicity (pKb) | pKb: 5.65 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -47.5×10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.404 |
| Dipole moment | 4.4317 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 359.7 J/mol·K |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -1089.2 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -1984 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | V03AB23 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Causes serious eye irritation. Causes skin irritation. May cause respiratory irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS05, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS05,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P305+P351+P338, P330, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 2-0-0 |
| Flash point | > 230 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 Oral Rat 2000 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral rat LD50 = 5200 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | NA7125000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL: Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 10 mg/m³ |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Not listed |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Methanesulfonic acid Ethanesulfonic acid Propane-1-sulfonic acid Pentanesulfonic acid Hexanesulfonic acid 1-Butanesulfonic acid 1-Butanesulfonic acid potassium salt Benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt |